Urinary cytokines after HCT: evidence for renal inflammation in the pathogenesis of proteinuria and kidney disease
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:

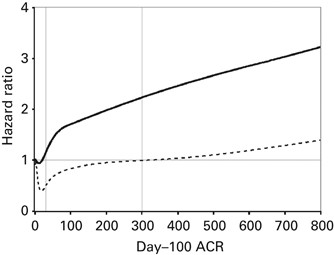
We compared urinary levels of cytokines in patients with and without albuminuria, proteinuria and kidney disease (glomerular filtration rate300, HR=2.82; 95% CI: 1.60–4.98). After HCT,
elevated urinary levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines are associated with development of albuminuria and proteinuria, suggesting early intra-renal inflammation as an important pathogenetic
mechanism. Albuminuria and proteinuria within the first 100 days post HCT are associated with decreased overall survival.
This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIDDK) 1R01DK080860-01. Chronic kidney disease in survivors of hematopoietic cell transplant received by Dr Hingorani.
Department of Pediatrics, Seattle Children’s Hospital/University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: