Systemic delivery of hk raf-1 sirna polyplexes inhibits mda-mb-435 xenografts
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:

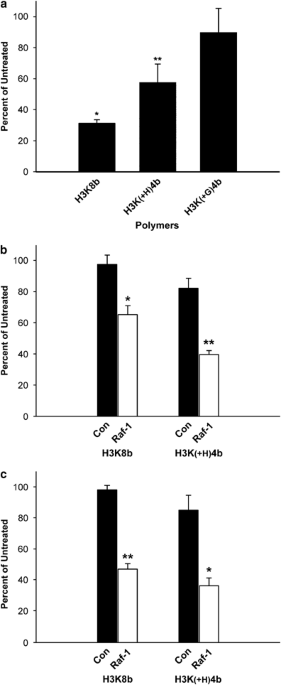
ABSTRACT Our past research has focused on identifying an effective carrier composed of histidine and lysine for delivery of nucleic acid into cells. For this purpose, we developed
histidine-lysine-rich (HK) polymers with specific sequences and branching. We have found that branched HK polymers in complex with Raf-1 siRNA markedly decreased Raf-1 mRNA and induced
apoptosis in cell lines _in vitro_. The primary focus of the present study was to determine an effective carrier to deliver siRNA systemically to tumor xenografts. After comparing HK:Raf-1
polyplexes for their _in-vivo_ efficacy, we investigated in greater detail whether one of these polymers, H3K(+H)4b, in complex with Raf-1 siRNA, inhibited the growth of MDA-MB-435
xenografts. H3K(+H)4b is a four-branched HK peptide whose predominant repeating sequence within the terminal arm is -HHHK-. After the first tail-vein injection in a mouse model, there was a
statistically significant reduction in tumor size between the H3K(+H)4b:Raf-1 siRNA-treated and the control groups (_P_<0.01). By the third injection, there was nearly a 50% reduction in
the Raf-1 siRNA-treated group compared to the control siRNA-treated or -untreated group. Consistent with a significant effect of the HK:Raf-1 polyplex on the tumor, there were marked
histological changes, increased apoptosis and fewer vessels in the Raf-1 siRNA-treated group. Raf-1 protein within the tumor was significantly decreased after treatment with the HK:Raf-1
siRNA polyplex compared to the control treatment groups. Despite the striking effect on the tumor by the HK Raf-1 siRNA, there was little evidence of toxicity in normal tissues with this
therapy. By harnessing the ability to modify the amino-acid sequence and branching of HK polymers, we expect continued development of HK polymers as _in-vivo_ carriers of siRNA. Access
through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices
may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support
SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS A PLATFORM TECHNOLOGY FOR ULTRA-LONG ACTING INTRATUMORAL THERAPY Article Open access 18 June 2024 INVESTIGATION OF THE ENHANCED ANTITUMOUR POTENCY OF
STING AGONIST AFTER CONJUGATION TO POLYMER NANOPARTICLES Article 13 July 2023 DIHYDROXYPHENYLALANINE-CONJUGATED HIGH MOLECULAR WEIGHT POLYETHYLENIMINE FOR TARGETED DELIVERY OF PLASMID
Article Open access 04 September 2024 REFERENCES * Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC . Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in
_Caenorhabditis elegans_. _Nature_ 1998; 391: 806–811. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Lorenz C, Hadwiger P, John M, Vornlocher HP, Unverzagt C . Steroid and lipid conjugates of
siRNAs to enhance cellular uptake and gene silencing in liver cells. _Bioorg Med Chem Lett_ 2004; 14: 4975–4977. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Takei Y, Kadomatsu K, Yuzawa Y,
Matsuo S, Muramatsu T . A small interfering RNA targeting vascular endothelial growth factor as cancer therapeutics. _Cancer Res_ 2004; 64: 3365–3370. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Hu-Lieskovan S, Heidel JD, Bartlett DW, Davis ME, Triche TJ . Sequence-specific knockdown of EWS-FLI1 by targeted, nonviral delivery of small interfering RNA inhibits tumor growth in a
murine model of metastatic Ewing's sarcoma. _Cancer Res_ 2005; 65: 8984–8992. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Heidel JD, Yu Z, Liu JY, Rele SM, Liang Y, Zeidan RK _et al_.
Administration in non-human primates of escalating intravenous doses of targeted nanoparticles containing ribonucleotide reductase subunit M2 siRNA. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 2007; 104:
5715–5721. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Bartlett DW, Davis ME . Physicochemical and biological characterization of targeted, nucleic acid-containing nanoparticles.
_Bioconjug Chem_ 2007; 18: 456–468. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Schiffelers RM, Ansari A, Xu J, Zhou Q, Tang Q, Storm G _et al_. Cancer siRNA therapy by tumor
selective delivery with ligand-targeted sterically stabilized nanoparticle. _Nucleic Acids Res_ 2004; 32: e149. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Li BJ, Tang Q, Cheng D, Qin
C, Xie FY, Wei Q _et al_. Using siRNA in prophylactic and therapeutic regimens against SARS coronavirus in Rhesus macaque. _Nat Med_ 2005; 11: 944–951. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Song E, Zhu P, Lee SK, Chowdhury D, Kussman S, Dykxhoorn DM _et al_. Antibody mediated _in vivo_ delivery of small interfering RNAs via cell-surface receptors. _Nat
Biotechnol_ 2005; 23: 709–717. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Leng Q, Goldgeier L, Zhu J, Cambell P, Ambulos N, Mixson AJ . Histidine-lysine peptides as carriers of nucleic acids.
_Drug News Perspect_ 2007; 20: 77–86. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Leng Q, Scaria P, Ioffe OB, Woodle M, Mixson AJ . A branched histidine/lysine peptide, H2K4b, in complex with
plasmids encoding antitumor proteins inhibits tumor xenografts. _J Gene Med_ 2006; 8: 1407–1415. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Leng Q, Scaria P, Zhu J, Ambulos N, Campbell P,
Mixson AJ . Highly branched HK peptides are effective carriers of siRNA. _J Gene Med_ 2005; 7: 977–986. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Leng Q, Mixson AJ . Small interfering RNA
targeting Raf-1 inhibits tumor growth _in vitro_ and _in vivo_. _Cancer Gene Ther_ 2005; 12: 682–690. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Chen QR, Zhang L, Luther PW, Mixson AJ . Optimal
transfection with the HK polymer depends on its degree of branching and the pH of endocytic vesicles. _Nucleic Acids Res_ 2002; 30: 1338–1345. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Chen QR, Zhang L, Stass SA, Mixson AJ . Co-polymer of histidine and lysine markedly enhances transfection of liposomes. _Gene Therapy_ 2000; 7: 698–704. Google Scholar * Yu W,
Pirollo KF, Yu B, Rait A, Xiang L, Huang W _et al_. Enhanced transfection efficiency of a systemically delivered tumor-targeting immunolipoplex by inclusion of a pH-sensitive histidylated
oligolysine peptide. _Nucleic Acids Res_ 2004; 32: e48. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Cioca DP, Aoki Y, Kiyosawa K . RNA interference is a functional pathway with
therapeutic potential in human myeloid leukemia cell lines. _Cancer Gene Ther_ 2003; 10: 125–133. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hood J, Granger HJ . Protein kinase G mediates
vascular endothelial growth factor-induced Raf-1 activation and proliferation in human endothelial cells. _J Biol Chem_ 1998; 273: 23504–23508. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Rudin
CM, Marshall JL, Huang CH, Kindler HL, Zhang C, Kumar D _et al_. Delivery of a liposomal c-raf-1 antisense oligonucleotide by weekly bolus dosing in patients with advanced solid tumors: a
phase I study. _Clin Cancer Res_ 2004; 10: 7244–7251. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Pei J, Zhang C, Gokhale PC, Rahman A, Dritschilo A, Ahmad I _et al_. Combination with
liposome-entrapped, ends-modified raf antisense oligonucleotide (LErafAON) improves the anti-tumor efficacies of cisplatin, epirubicin, mitoxantrone, docetaxel and gemcitabine. _Anticancer
Drugs_ 2004; 15: 243–253. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Grugel S, Finkenzeller G, Weindel K, Barleon B, Marme D . Both v-Ha-Ras and v-Raf stimulate expression of the vascular
endothelial growth factor in NIH 3T3 cells. _J Biol Chem_ 1995; 270: 25915–25919. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Hood JD, Frausto R, Kiosses WB, Schwartz MA, Cheresh DA .
Differential alphav integrin-mediated Ras-ERK signaling during two pathways of angiogenesis. _J Cell Biol_ 2003; 162: 933–943. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Khatib
AM, Fallavollita L, Wancewicz EV, Monia BP, Brodt P . Inhibition of hepatic endothelial E-selectin expression by C-raf antisense oligonucleotides blocks colorectal carcinoma liver
metastasis. _Cancer Res_ 2002; 62: 5393–5398. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Leng Q, Kahn J, Zhu J, Scaria P, Mixson J . Needle-like morphology of H2K4b polyplexes associated with increases
in transfection _in vitro_. _Cancer Ther_ 2007; 5B: 193–202. PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Chen QR, Zhang L, Stass SA, Mixson AJ . Branched co-polymers of histidine and lysine
are efficient carriers of plasmids. _Nucleic Acids Res_ 2001; 29: 1334–1340. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Hood JD, Bednarski M, Frausto R, Guccione S, Reisfeld RA,
Xiang R _et al_. Tumor regression by targeted gene delivery to the neovasculature. _Science_ 2002; 296: 2404–2407. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bellocq NC, Pun SH, Jensen GS,
Davis ME . Transferrin-containing, cyclodextrin polymer-based particles for tumor-targeted gene delivery. _Bioconjug Chem_ 2003; 14: 1122–1132. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kunath
K, Merdan T, Hegener O, Haberlein H, Kissel T . Integrin targeting using RGD-PEI conjugates for _in vitro_ gene transfer. _J Gene Med_ 2003; 5: 588–599. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We are grateful to Dr Pamela Talalay for her careful reading and useful comments concerning the article. We thank Dr Nicholas Ambulos and Dr Pat
Campbell of the Maryland Biopolymer laboratory for synthesizing the peptides in this study. This study was supported by the National Cancer Institute CA70394. AUTHOR INFORMATION Author notes
* P Scaria & M C Woodle Present address: 4Current Address: Aparna Biosciences, Rockville, MD 20852, USA., AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Pathology, University of Maryland,
Baltimore, MD, USA Q Leng & A J Mixson * Intradigm Corporation, Palo Alto, CA, USA P Scaria & M C Woodle * Sirnaomics Inc., Gaithersburg, MD, USA P Lu Authors * Q Leng View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * P Scaria View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * P Lu View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M C Woodle View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * A J Mixson View
author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to A J Mixson. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS
ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Leng, Q., Scaria, P., Lu, P. _et al._ Systemic delivery of HK Raf-1 siRNA polyplexes inhibits MDA-MB-435 xenografts. _Cancer Gene Ther_ 15, 485–495 (2008).
https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2008.29 Download citation * Received: 14 November 2007 * Revised: 03 February 2008 * Accepted: 08 March 2008 * Published: 16 May 2008 * Issue Date: August 2008 *
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2008.29 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * Histidine * lysine * peptides * Raf-1 * tumor xenograft