Yohimbine relaxes the human corpus cavernosum through a non-adrenergic mechanism involving the activation of k+atp-dependent channels
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:

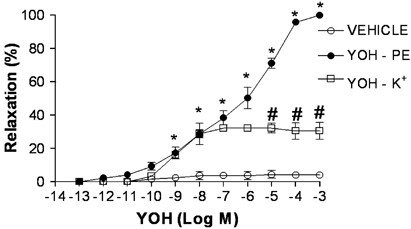
ABSTRACT The mechanism by which yohimbine relaxes the human corpus cavernosum remains unclear. Using the human corpus cavernosum strips immersed in isometric baths containing Krebs–Henseleit
solution, this study investigates the effect of yohimbine on the relaxation of the human corpus cavernosum through nitrergic pathways involving the activation of ATP-dependent potassium
channels (KATP). The maximal relaxation induced by yohimbine in the human corpus cavernosum strips pre-contracted with phenylephrine was 100±0% and only 30.5±5.0% when they were
pre-contracted with 60-mM potassium (K+) solution. The maximal relaxation induced by yohimbine in phenylephrine pre-contracted tissues was significantly inhibited by tetrodotoxin, 1H-[1,2,4]
oxadiazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one (ODQ) or 7-nitroindazole (43.6, 36.1 and 42.6%, respectively). Neither the combination charybdotoxin–apamin nor tetraethylammonium altered the response of
the human corpora cavernosa strips to yohimbine. Nevertheless, glibenclamide decreased the maximum relaxant response to yohimbine by 29.8% (_P_<0.05; _n_=12). The results suggest that
yohimbine relaxes the human corpus cavernosum by a non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic mechanism, probably activating the nitrergic-soluble guanylate cyclase (NO-sGc) pathway and KATP. Access
through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $21.58 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices
may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support
SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS IN VITRO EFFECT OF RELAXIN IN THE RAT CORPUS CAVERNOSUM UNDER HYPERGLYCEMIC AND NORMOGLYCEMIC CONDITIONS Article 12 December 2022 INHIBITORY MECHANISMS
OF DOCOSAHEXAENOIC ACID ON CARBACHOL-, ANGIOTENSIN II-, AND BRADYKININ-INDUCED CONTRACTIONS IN GUINEA PIG GASTRIC FUNDUS SMOOTH MUSCLE Article Open access 22 May 2024 LACOSAMIDE ALLEVIATES
BILATERAL CAVERNOUS NERVE INJURY-INDUCED ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION IN THE RAT MODEL BY AMELIORATING PATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE CORPUS CAVERNOSUM Article 15 March 2023 REFERENCES * Feldman HA,
Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, Krane RJ, McKinlay JB . Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. _J Urol_ 1994; 15: 54–61. Article
Google Scholar * Andersson KE, Wagner G . Physiology of penile erection. _Physiol Rev_ 1995; 75: 191–236. Article CAS Google Scholar * Fallon B . ‘Off-label’ drug use in sexual
medicine treatment. _Int J Impot Res_ 2007; 20: 127–134. Article Google Scholar * Filippi S, Luconi M, Granchi S, Natali A, Tozzi P, Forti G _et al_. Endotheliumdependency of
yohimbine-induced corpus cavernosum relaxation. _Int J Impot Res_ 2002; 14: 295–307. Article CAS Google Scholar * Traish A, Gupta S, Gallant C, Huang Y-H, Goldstein I . Phentolamine
mesylate relaxes penile corpus cavernosum tissue by adrenergic and non-adrenergic mechanisms. _Int J Impot Res_ 1998; 10: 215–223. Article CAS Google Scholar * Tam SW, Worcel M, Wylle M .
Yoimbine: a clinical review. _Pharmacol Ther_ 2001; 91: 215–243. Article CAS Google Scholar * Glina S, Martins FG, Damião R . Tratamento oral. In: I Consenso Brasileiro de disfunção
erétil (ed). _BG cultural_. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1998, pp, 63–70. Google Scholar * Stanislavov R, Nikolova V, Rohdewald P . Improvement of erectile function with Prelox: a randomized,
double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. _Int J Impot Res_ 2007; 20: 173–180. Article Google Scholar * Traish AM, Moreland RB, Huang YH, Goldstein I . Expression of functional
α2- adrenergic receptor subtypes in human corpus cavernosum and in cultured trabecular smooth muscle cells. _Recept Signal Transduct_ 1997; 7: 55–67. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kim NN,
Goldstein I, Moreland RB, Traish AM . Alpha-adrenergic receptor blockade by phentolamine increases the eficacy of vasodilators in penile corpus cavernosum. _Int J Impot Res_ 2000; 12 (Suppl
1): S26–S36. Article Google Scholar * Silva LF, Nascimento NR, Fonteles MC, de Nucci G, Moraes ME, Vasconcelos PR _et al_. Phentolamine relaxes human corpus cavernosum by a non-adrenergic
mechanism activating ATP-sensitive K+ channel. _Int J Impot Res_ 2005; 17: 27–32. Article CAS Google Scholar * Hellstrom WJG . Clinical applications of centrally acting agents in male
sexual dysfunction. _Int J Impot Res_ 2008; 20: S17–S23. Article CAS Google Scholar * Senbel AM, Mostafa T . Yohimbine enhances the effect of sildenafil on erectile process in rats. _Int
J Impot Res_ 2008; 20: 409–417. Article CAS Google Scholar * Saenz de Tejada I, Garvey DS, Schroeder JD, Shelekhin TL, Letts G, Fernandez A _et al_. Design and evaluation of nitrosylated
α-adrenergic receptor antagonists as potential agents for the treatment of impotence. _Pharmacol Exp Ther_ 1999; 290: 121–128. Google Scholar * Saenz de Tejada I . Molecular mechanisms for
the regulation of penile smooth muscle contractility. _Int J Impot Res_ 2002; 14 (Suppl 1): S6–S10. Article Google Scholar * Molderings GJ, Göthert M, Van Ahlen H, Porst H . Noradrenaline
release in human corpus cavernosum and its modulation via presynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptors. _Fundam Clin Pharmacol_ 1989; 3: 497–504. Article CAS Google Scholar * Saenz De Tejada I, Kim
NN, Goldstein I, Traish AM . Regulation of pre-synaptic alpha-adrenergic activity in the corpus cavernosum. _Int J Impot Res_ 2000; 12 (Suppl 1): S20–S25. Article Google Scholar * Archer
SL . Potassium channels and erectile dysfunction. _Vasc Pharmacol_ 2002; 38: 61–71. Article CAS Google Scholar * Spector M, Rodriguez R, Rosenbaum RS, Wang HZ, Melman A, Christ GJ .
Potassium channels and human corporeal smooth muscle cell tone: further evidence of the physiological relevance of the maxi-K channel subtype to the regulation of human corporeal smooth
muscle tone _in vitro_. _J Urol_ 2002; 167: 2628–2635. Article Google Scholar * Stumpff F, Strauss O, Boxberger M, Wiederholt M . Characterization of maxi-channels in bovine trabecular
meshwork and their activation by cyclic guanosine monophosphate. _Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci_ 1997; 38: 1883–1892. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Fanh SF, Brink PR, Melmann A, Christ GJ . An
analysis of the Maxi-K+ (Kca) channel in cultured human corporal smooth muscle cells. _J Urol_ 1995; 153: 818–825. Article Google Scholar * Venkateswarlu K, Giraldi A, Zhao W, Wang HZ,
Melman A, Spektor M _et al_. Potassium channels and human corporeal smooth muscle cell tone: diabetes and relaxation of human corpus cavernosum smooth muscle by adenosine thiphosphate
sensitive potassium channel operners. _J Urol_ 2002; 168: 355–361. Article CAS Google Scholar * El-Metwally MA, Sharabi FM, Daabees TT, Senbel AM, Mostafa T . Involvement of
alpha-receptors and potassium channels in the mechanism of action of sildenafil citrate. _Int J Impot Res_ 2007; 19: 551–557. Article CAS Google Scholar * Campos AR, Cunha KMA, Santos FA,
Silveira ER, Uchoa DEA, Nascimento NRF, Rao VSN . Relaxant effects of an alkaloid-rich fraction from Aspidosperma ulei root bark on isolated rabbit corpus cavernosum. _Int J Impot Res_
2007; 20: 255–263. Article Google Scholar Download references AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Surgery Division Urology, Ceara Federal University, Fortaleza, Ceara, Brazil F C
Freitas, N R F Nascimento, J B G Cerqueira, M E A Morais, R P Regadas & L F Gonzaga-Silva Authors * F C Freitas View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed
Google Scholar * N R F Nascimento View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * J B G Cerqueira View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar * M E A Morais View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * R P Regadas View author publications You can also search
for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * L F Gonzaga-Silva View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to F C
Freitas. RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Freitas, F., Nascimento, N., Cerqueira, J. _et al._ Yohimbine relaxes the human corpus
cavernosum through a non-adrenergic mechanism involving the activation of K+ATP-dependent channels. _Int J Impot Res_ 21, 356–361 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2009.41 Download
citation * Received: 16 March 2009 * Revised: 06 August 2009 * Accepted: 06 August 2009 * Published: 17 September 2009 * Issue Date: November 2009 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2009.41
SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy
to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * yohimbine * human corpus cavernosum * erectile dysfunction * K+ channels