Imaging of neutral lipids by oil red O for analyzing the metabolic status in health and disease
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:

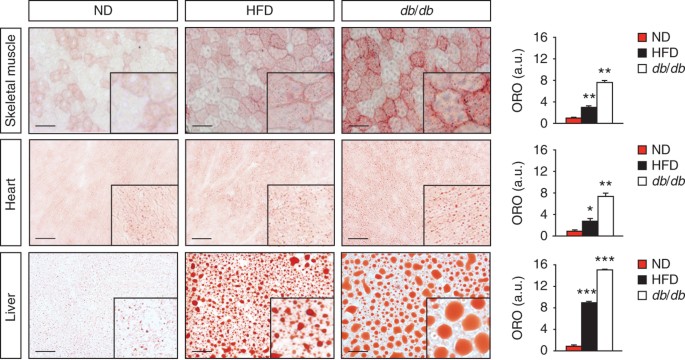
Excess lipid accumulation in peripheral tissues is a key feature of many metabolic diseases. Therefore, techniques for imaging and quantifying lipids in various tissues are important for
understanding and evaluating the overall metabolic status of a research subject. Here we present a protocol that detects neutral lipids and lipid droplet (LD) morphology by oil red O (ORO)
staining of sections from frozen tissues. The method allows for easy estimation of tissue lipid content and distribution using only basic laboratory and computer equipment. Furthermore, the
procedure described here is well suited for the comparison of different metabolically challenged animal models. As an example, we include data on muscular and hepatic lipid accumulation in
diet-induced and genetically induced diabetic mice. The experimental description presents details for optimal staining of lipids using ORO, including tissue collection, sectioning, staining,
imaging and measurements of tissue lipids, in a time frame of less than 2 d.
We want to thank S. Wittgren, E. Cortez and C. Mössinger for technical assistance. This study was supported by The Novo Nordisk Foundation, The Swedish Cancer Foundation, The Swedish
Research Council, Torsten och Ragnar Söderbergs Stiftelser, The Peter Wallenberg Foundation for Economics and Technology, The Swedish Heart and Lung Foundation, Ludwig Institute for Cancer
Research and Karolinska Institutet. C.E.H. was kindly supported by Frans Wilhelm och Waldemar von Frenckells Fond and by Wilhelm och Else Stockmanns Stiftelse.
Division of Vascular Biology, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics, Tissue Biology Group, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden
Annika Mehlem, Carolina E Hagberg, Lars Muhl, Ulf Eriksson & Annelie Falkevall
A.M. performed in vivo mouse experiments, ORO analyses and wrote the paper; C.E.H. optimized the protocol and commented on the paper; L.M. commented on the paper; U.E. commented on the
paper; A.F. optimized the protocol, performed ORO analyses, assisted in in vivo mouse studies and wrote the paper. All the authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: