Diet and tumor lkb1 expression interact to determine sensitivity to anti-neoplastic effects of metformin in vivo
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:

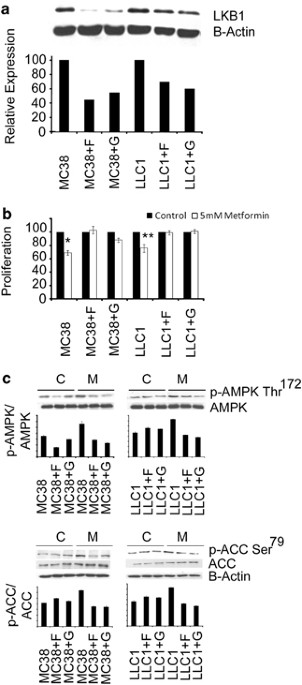
ABSTRACT Hypothesis-generating epidemiological research has suggested that cancer burden is reduced in diabetics treated with metformin and experimental work has raised questions regarding
the role of direct adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-mediated anti-neoplastic effects of metformin as compared with indirect effects attributable to reductions in
circulating insulin levels in the host. We treated both tumor LKB1 expression and host diet as variables, and observed that metformin inhibited tumor growth and reduced insulin receptor
activation in tumors of mice with diet-induced hyperinsulinemia, independent of tumor LKB1 expression. In the absence of hyperinsulinemia, metformin inhibited only the growth of tumors
transfected with short hairpin RNA against LKB1, a finding attributable neither to an effect on host insulin level nor to activation of AMPK within the tumor. Further investigation _in
vitro_ showed that cells with reduced LKB1 expression are more sensitive to metformin-induced adenosine triphosphate depletion owing to impaired ability to activate LKB1-AMPK-dependent
energy-conservation mechanisms. Thus, loss of function of LKB1 can accelerate proliferation in contexts where it functions as a tumor suppressor, but can also sensitize cells to metformin.
These findings predict that any clinical utility of metformin or similar compounds in oncology will be restricted to subpopulations defined by host insulin levels and/or loss of function of
LKB1. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this
journal Receive 50 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $5.18 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer
support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS A PRECISION MEDICINE APPROACH TO METABOLIC THERAPY FOR BREAST CANCER IN MICE Article Open access 20 May 2022 THE EFFECTS OF GLYCEMIC INDEX ON
PROSTATE CANCER PROGRESSION IN A XENOGRAFT MOUSE MODEL Article Open access 11 December 2023 CALORIC RESTRICTION LEADS TO DRUGGABLE LSD1-DEPENDENT CANCER STEM CELLS EXPANSION Article Open
access 27 January 2024 REFERENCES * Algire C, Amrein L, Zakikhani M, Panasci L, Pollak M . (2010). Metformin blocks the stimulative effect of a high energy diet on colon carcinoma growth _in
vivo_ and is associated with reduced expression of fatty acid acid synthase. _Endocr Relat Cancer_ 17: 351–360. Article CAS Google Scholar * Algire C, Zakikhani M, Blouin M-J, Shuai JH,
Pollak M . (2008). Metformin attenuates the stimulatory effect of a high energy diet on _in vivo_ H59 carcinoma growth. _Endocr Relat Cancer_ 15: 833–839. Article CAS Google Scholar *
Blake DA, McLean NV . (1989). A colorimetric assay for the measurement of -glucose consumption by cultured cells. _Anal Biochem_ 177: 156–160. Article CAS Google Scholar * Bodmer M, Meier
C, Krahenbuhl S, Jick SS, Meier CR, Meier CR . (2010). Long-term metformin use is associated with decreased risk of breast cancer. _Diabetes Care_ 33: 1304–1308. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Buzzai M, Jones RG, Amaravadi RK, Lum JJ, DeBerardinis RJ, Zhao F _et al_. (2007). Systemic treatment with the antidiabetic drug metformin selectively impairs p53-deficient tumor
cell growth. _Cancer Res_ 67: 6745–6752. Article CAS Google Scholar * Currie CJ, Poole CD, Gale EA . (2009). The influence of glucose-lowering therapies on cancer risk in type 2 diabetes.
_Diabetologia_ 52: 1766–1777. Article CAS Google Scholar * DeFronzo RA, Goodman AM . (1995). Efficacy of metformin in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The
Multicenter Metformin Study Group. _N Engl J Med_ 333: 541–549. Article CAS Google Scholar * Dowling RJ, Zakikhani M, Fantus IG, Pollak M, Sonenberg N . (2007). Metformin inhibits
mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent translation initiation in breast cancer cells. _Cancer Res_ 67: 10804–10812. Article CAS Google Scholar * Dykens JA, Jamieson J, Marroquin L,
Nadanaciva S, Billis PA, Will Y . (2008). Biguanide-induced mitochondrial dysfunction yields increased lactate production and cytotoxicity of aerobically-poised HepG2 cells and human
hepatocytes _in vitro_. _Toxicol Appl Pharmacol_ 233: 203–210. Article CAS Google Scholar * Engelman, Cantley . (2010). Chemoprevention meets glucose control. _Can Prev Res_ 3: 1049–1052.
Article CAS Google Scholar * El Mir MY, Nogueira V, Fontaine E, Averet N, Rigoulet M, Leverve X . (2000). Dimethylbiguanide inhibits cell respiration via an indirect effect targeted on
the respiratory chain complex I. _J Biol Chem_ 275: 223–228. Article CAS Google Scholar * Evans JM, Donnelly LA, Emslie-Smith AM, Alessi DR, Morris AD . (2005). Metformin and reduced risk
of cancer in diabetic patients. _BMJ_ 330: 1304–1305. Article Google Scholar * Fantin VR, St Pierre J, Leder P . (2006). Attenuation of LDH-A expression uncovers a link between
glycolysis, mitochondrial physiology, and tumor maintenance. _Cancer Cell_ 9: 425–434. Article CAS Google Scholar * Foretz M, Hebrard S, Leclerc J, Zarrinpashneh E, Soty M, Mithieux G _et
al_. (2010). Metformin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis in mice independently of the LKB1/AMPK pathway via a decrease in hepatic energy state. _J Clin Invest_ 120: 2267–2270. Article
Google Scholar * Hardie DG . (2006). Neither LKB1 nor AMPK are the direct targets of metformin. _Gastroenterology_ 131: 973. Article Google Scholar * Hardie DG . (2007).
AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinases: conserved guardians of cellular energy. _Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol_ 8: 774–785. Article CAS Google Scholar * Hosono K, Endo H, Takahashi H, Sugiyama M,
Sakai E, Uchiyama T _et al_. (2007). Metformin suppresses colorectal aberrant crypt foci in a short-term clinical trial. _Can Prev Res_ 3: 1077–1083. Article Google Scholar * Huang X,
Wullschleger S, Shpiro N, McGuire VA, Sakamoto K, Woods YL _et al_. (2008). Important role of the LKB1-AMPK pathway in suppressing tumourigenesis in PTEN deficient mice. _Biochem J_ 412:
211–221. Article CAS Google Scholar * Ji H, Ramsey MR, Hayes DN, Fan C, McNamara K, Kozlowski P _et al_. (2007). LKB1 modulates lung cancer differentiation and metastasis. _Nature_ 448:
807–810. Article CAS Google Scholar * Jones RG, Plas DR, Kubek S, Buzzai M, Mu J, Xu Y _et al_. (2005). AMP-activated protein kinase induces a p53-dependent metabolic checkpoint. _Mol
Cell_ 18: 283–293. Article CAS Google Scholar * Kalaany NY, Sabatini DM . (2009). Tumours with PI3K activation are resistant to dietary restriction. _Nature_ 458: 725–731. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Kalender A, Selvaraj A, Kim SY, Gulati P, Brule S, Viollet B _et al_. (2010). Metformin, independent of AMPK, inhibits mTORC1 in a rag GTPase-dependent manner. _Cell Metab_
11: 390–401. Article CAS Google Scholar * Kroemer G, Pouyssegur J . (2008). Tumor cell metabolism: cancer's Achilles’ heel. _Cancer Cell_ 13: 472–482. Article CAS Google Scholar
* Landman GW, Kleefstra N, van Hateren KJ, Groenier KH, Gans RO, Bilo HJ . (2010). Metformin associated with lower cancer mortality in type 2 diabetes: ZODIAC-16. _Diabetes Care_ 33:
322–326. Article CAS Google Scholar * Larsson SC, Mantzoros CS, Wolk A . (2007). Diabetes mellitus and risk of breast cancer: a meta-analysis. _Int J Cancer_ 121: 856–862. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Larsson SC, Orsini N, Wolk A . (2005). Diabetes mellitus and risk of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. _J Natl Cancer Inst_ 97: 1679–1687. Article Google Scholar *
Libby G, Donnelly LA, Donnan PT, Alessi DR, Morris AD, Evans JM . (2009). New users of metformin are at low risk of incident cancer: a cohort study among people with type 2 diabetes.
_Diabetes Care_ 32: 1620–1625. Article CAS Google Scholar * Liu B, Fan Z, Edgerton SM, Deng XS, Alimova IN, Lind SE _et al_. (2009). Metformin induces unique biological and molecular
responses in triple negative breast cancer cells. _Cell Cycle_ 8: 2031–2040. Article CAS Google Scholar * Memmott RM, Mercado JR, Maier CR, Kawabata S, Fox SD, Dennis PA . (2010).
Metformin prevents tobacco carcinogen-induced lung tumorigenesis. _Can Prev Res_ 3: 1066–1076. Article CAS Google Scholar * Novosyadlyy R, Lann DE, Vijayakumar A, Rowzee A, Lazzarino DA,
Fierz Y _et al_. (2010). Insulin-mediated acceleration of breast cancer development and progression in a nonobese model of type 2 diabetes. _Cancer Res_ 70: 741–751. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Owen MR, Doran E, Halestrap AP . (2000). Evidence that metformin exerts its anti-diabetic effects through inhibition of complex 1 of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. _Biochem
J_ 348 (Part 3): 607–614. Article CAS Google Scholar * Pollak M . (2008). Insulin and insulin-like growth factor signalling in neoplasia. _Nat Rev Cancer_ 8: 915–928. Article CAS Google
Scholar * Pollak M . (2009). Do cancer cells care if their host is hungry? _Cell Metab_ 9: 401–403. Article CAS Google Scholar * Pollak M . (2010). Metformin and other biguanides in
oncology: advancing the research agenda. _Can Prev Res_ 3: 1060–1065. Article CAS Google Scholar * Russell III RR, Li J, Coven DL, Pypaert M, Zechner C, Palmeri M _et al_. (2004).
AMP-activated protein kinase mediates ischemic glucose uptake and prevents postischemic cardiac dysfunction, apoptosis, and injury. _J Clin Invest_ 114: 495–503. Article CAS Google Scholar
* Sakamoto K, McCarthy A, Smith D, Green KA, Grahame HD, Ashworth A _et al_. (2005). Deficiency of LKB1 in skeletal muscle prevents AMPK activation and glucose uptake during contraction.
_EMBO J_ 24: 1810–1820. Article CAS Google Scholar * Sanchez-Cespedes M, Parrella P, Esteller M, Nomoto S, Trink B, Engles JM _et al_. (2002). Inactivation of LKB1/STK11 is a common event
in adenocarcinomas of the lung. _Cancer Res_ 62: 3659–3662. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Shackelford DB, Shaw RJ . (2009). The LKB1-AMPK pathway: metabolism and growth control in tumour
suppression. _Nat Rev Cancer_ 9: 563–575. Article CAS Google Scholar * Shaw RJ, Kosmatka M, Bardeesy N, Hurley RL, Witters LA, Depinho RA _et al_. (2004). The tumor suppressor LKB1 kinase
directly activates AMP-activated kinase and regulates apoptosis in response to energy stress. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 101: 3329–3335. Article CAS Google Scholar * Shaw RJ, Lamia KA,
Vasquez D, Koo SH, Bardeesy N, Depinho RA _et al_. (2005). The kinase LKB1 mediates glucose homeostasis in liver and therapeutic effects of metformin. _Science_ 310: 1642–1646. Article CAS
Google Scholar * Tennant DA, Duran RV, Gottlieb E . (2010). Targeting metabolic transformation for cancer therapy. _Nat Rev Cancer_ 10: 267–277. Article CAS Google Scholar * Tomimoto
A, Endo H, Sugiyama M, Fujisawa T, Hosono K, Takahashi H _et al_. (2008). Metformin suppresses intestinal polyp growth in ApcMin/+ mice. _Cancer Sci_ 99: 2136–2141. Article CAS Google
Scholar * van Lier MG, Wagner A, Mathus-Vliegen EM, Kuipers EJ, Steyerberg EW, van Leerdam ME . (2010). High cancer risk in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: a systematic review and surveillance
recommendations. _Am J Gastroenterol_ 105: 1258–1264. Article CAS Google Scholar * Venkateswaran V, Haddad AQ, Fleshner NE, Fan R, Sugar LM, Nam R _et al_. (2007). Association of
diet-induced hyperinsulinemia with accelerated growth of prostate cancer (LNCaP) xenografts. _J Natl Cancer Inst_ 99: 1793–1800. Article Google Scholar * Vigneri P, Frasca F, Sciacca L,
Pandini G, Vigneri R . (2009). Diabetes and cancer. _Endocr Relat Cancer_ 16: 1103–1123. Article CAS Google Scholar * Wingo SN, Gallardo TD, Akbay EA, Liang MC, Contreras CM, Boren T _et
al_. (2009). Somatic LKB1 mutations promote cervical cancer progression. _PLoS One_ 4: e5137. Article Google Scholar * Zakikhani M, Dowling R, Fantus IG, Sonenberg N, Pollak M . (2006).
Metformin is an AMP kinase-dependent growth inhibitor for breast cancer cells. _Cancer Res_ 66: 10269–10273. Article CAS Google Scholar * Zakikhani M, Dowling RJ, Sonenberg N, Pollak MN .
(2008). The effects of adiponectin and metformin on prostate and colon neoplasia involve activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. _Cancer Prev Res (Phila, PA)_ 1: 369–375. Article CAS
Google Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank Dr André Veillette for his advice and technical expertise, Dr Pnina Brodt for the MC38 cells, Drs Lawrence Panasci and Ernesto
Schiffrin for sharing laboratory resources, and Dr Nahum Sonenberg and Dr Russell Jones for reviewing the manuscript prior to submission. This work was supported by a grant from the Terry
Fox Research Institute. Ms Algire is supported through the Montréal Centre for Experimental Therapeutics in Cancer student fellowship and the Canadian Institute of Health Research Canada
Graduate Fellowship. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Departments of Experimental Medicine and Oncology, E423 Segal Cancer Centre of the Jewish General Hospital, McGill
University, Montréal, Québec, Canada C Algire & M Pollak * Lady Davis Institute for Medical Research, Jewish General Hospital, Montréal, Québec, Canada L Amrein, M Bazile, S David &
M Zakikhani Authors * C Algire View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * L Amrein View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * M Bazile View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * S David View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * M Zakikhani View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M Pollak View author publications You can also search for this
author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to M Pollak. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no conflict of interest. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1A (PDF 90 KB) SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1B (PDF 133 KB) SUPPLEMENTARY
FIGURE LEGEND (DOC 22 KB) SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (DOC 21 KB) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Algire, C., Amrein, L., Bazile, M. _et
al._ Diet and tumor LKB1 expression interact to determine sensitivity to anti-neoplastic effects of metformin _in vivo_. _Oncogene_ 30, 1174–1182 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.483
Download citation * Received: 08 July 2010 * Revised: 01 September 2010 * Accepted: 13 September 2010 * Published: 22 November 2010 * Issue Date: 10 March 2011 * DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.483 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative KEYWORDS * metformin * insulin * cancer * LKB1