A novel protein isoform of the ron tyrosine kinase receptor transforms human pancreatic duct epithelial cells
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:

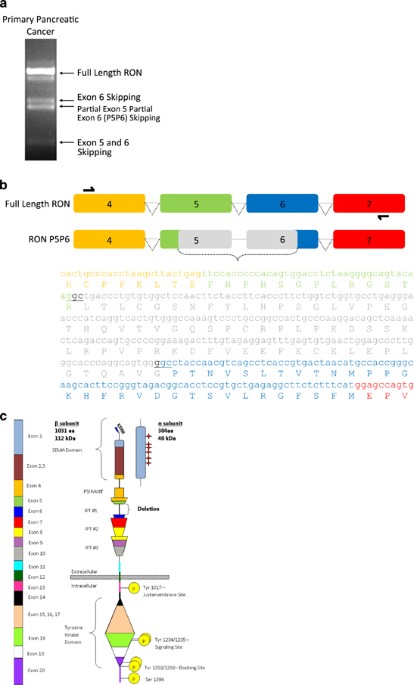
ABSTRACT The _MST1R_ gene is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer producing elevated levels of the RON tyrosine kinase receptor protein. While mutations in _MST1R_ are rare, alternative splice
variants have been previously reported in epithelial cancers. We report the discovery of a novel RON isoform discovered in human pancreatic cancer. Partial splicing of exons 5 and 6 (P5P6)
produces a RON isoform that lacks the first extracellular immunoglobulin-plexin-transcription domain. The splice variant is detected in 73% of xenografts derived from pancreatic
adenocarcinoma patients and 71% of pancreatic cancer cell lines. Peptides specific to RON P5P6 detected in human pancreatic cancer specimens by mass spectrometry confirm translation of the
protein isoform. The P5P6 isoform is found to be constitutively phosphorylated, present in the cytoplasm, and it traffics to the plasma membrane. Expression of P5P6 in immortalized human
pancreatic duct epithelial (HPDE) cells activates downstream AKT, and in human pancreatic epithelial nestin-expressing cells, activates both the AKT and MAPK pathways. Inhibiting RON P5P6 in
HPDE cells using a small molecule inhibitor BMS-777607 blocked constitutive activation and decreased AKT signaling. P5P6 transforms NIH3T3 cells and induces tumorigenicity in HPDE cells.
Resultant HPDE-P5P6 tumors develop a dense stromal compartment similar to that seen in pancreatic cancer. In summary, we have identified a novel and constitutively active isoform of the RON
tyrosine kinase receptor that has transforming activity and is expressed in human pancreatic cancer. These findings provide additional insight into the biology of the RON receptor in
pancreatic cancer and are clinically relevant to the study of RON as a potential therapeutic target. Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription
content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this journal Receive 50 print issues and online access $259.00 per year only $5.18 per issue
Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL
ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS SCAMP3 IS A MUTANT EGFR PHOSPHORYLATION
TARGET AND A TUMOR SUPPRESSOR IN LUNG ADENOCARCINOMA Article 13 April 2021 NARDILYSIN-REGULATED SCISSION MECHANISM ACTIVATES POLO-LIKE KINASE 3 TO SUPPRESS THE DEVELOPMENT OF PANCREATIC
CANCER Article Open access 11 April 2024 _KRAS_ MUTATION RATE PRECISELY ORCHESTRATES DUCTAL DERIVED PANCREATIC INTRAEPITHELIAL NEOPLASIA AND PANCREATIC CANCER Article Open access 02 October
2020 REFERENCES * Ronsin C, Muscatelli F, Mattei MG, Breathnach R . A novel putative receptor protein tyrosine kinase of the met family. _Oncogene_ 1993; 8: 1195–1202. CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Benight NM, Waltz SE . Ron receptor tyrosine kinase signaling as a therapeutic target. _Expert Opin Ther Targets_ 2012; 16: 921–931. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google
Scholar * Wang X, Hankey PA . The ron receptor tyrosine kinase: a key regulator of inflammation and cancer progression. _Crit Rev Immunol_ 2013; 33: 549–574. Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Gurusamy D, Gray JK, Pathrose P, Kulkarni RM, Finkleman FD, Waltz SE . Myeloid-specific expression of Ron receptor kinase promotes prostate tumor growth. _Cancer Res_ 2013; 73:
1752–1763. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * O'Toole JM, Rabenau KE, Burns K, Lu D, Mangalampalli V, Balderes P _et al_. Therapeutic implications of a human
neutralizing antibody to the macrophage-stimulating protein receptor tyrosine kinase (RON), a c-MET family member. _Cancer Res_ 2006; 66: 9162–9170. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Schroeder GM, An Y, Cai ZW, Chen XT, Clark C, Cornelius LA _et al_. Discovery of
N-(4-(2-amino-3-chloropyridin-4-yloxy)-3-fluorophenyl)-4-ethoxy-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridine-3-carboxamide (BMS-777607), a selective and orally efficacious inhibitor of the
Met kinase superfamily. _J Med Chem_ 2009; 52: 1251–1254. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Thomas RM, Toney K, Fenoglio-Preiser C, Revelo-Penafiel MP, Hingorani SR, Tuveson DA _et
al_. The RON receptor tyrosine kinase mediates oncogenic phenotypes in pancreatic cancer cells and is increasingly expressed during pancreatic cancer progression. _Cancer Res_ 2007; 67:
6075–6082. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Camp ER, Yang A, Gray MJ, Fan F, Hamilton SR, Evans DB _et al_. Tyrosine kinase receptor RON in human pancreatic cancer: expression,
function, and validation as a target. _Cancer_ 2007; 109: 1030–1039. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Logan-Collins J, Thomas RM, Yu P, Jaquish D, Mose E, French R _et al_. Silencing
of RON receptor signaling promotes apoptosis and gemcitabine sensitivity in pancreatic cancers. _Cancer Res_ 2010; 70: 1130–1140. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Wang
J, Rajput A, Kan JL, Rose R, Liu XQ, Kuropatwinski K _et al_. Knockdown of Ron kinase inhibits mutant phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and reduces metastasis in human colon carcinoma. _J Biol
Chem_ 2009; 284: 10912–10922. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Feres KJ, Ischenko I, Hayman MJ . The RON receptor tyrosine kinase promotes MSP-independent cell
spreading and survival in breast epithelial cells. _Oncogene_ 2009; 28: 279–288. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Wang MH, Ronsin C, Gesnel MC, Coupey L, Skeel A, Leonard EJ _et al_.
Identification of the ron gene product as the receptor for the human macrophage stimulating protein. _Science_ 1994; 266: 117–119. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Angeloni D,
Danilkovitch-Miagkova A, Miagkov A, Leonard EJ, Lerman MI . The soluble sema domain of the RON receptor inhibits macrophage-stimulating protein-induced receptor activation. _J Biol Chem_
2004; 279: 3726–3732. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Chao KL, Tsai IW, Chen C, Herzberg O . Crystal structure of the Sema-PSI extracellular domain of human RON receptor tyrosine
kinase. _PLoS One_ 2012; 7: e41912. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Yao HP, Zhou YQ, Zhang R, Wang MH . MSP-RON signalling in cancer: pathogenesis and therapeutic
potential. _Nat Rev Cancer_ 2013; 13: 466–481. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Collesi C, Santoro MM, Gaudino G, Comoglio PM . A splicing variant of the RON transcript induces
constitutive tyrosine kinase activity and an invasive phenotype. _Mol Cell Biol_ 1996; 16: 5518–5526. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Zhou YQ, He C, Chen YQ, Wang D,
Wang MH . Altered expression of the RON receptor tyrosine kinase in primary human colorectal adenocarcinomas: generation of different splicing RON variants and their oncogenic potential.
_Oncogene_ 2003; 22: 186–197. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Bardella C, Costa B, Maggiora P, Patane' S, Olivero M, Ranzani GN _et al_. Truncated RON tyrosine kinase drives
tumor cell progression and abrogates cell-cell adhesion through E-cadherin transcriptional repression. _Cancer Res_ 2004; 64: 5154–5161. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Liu X, Zhao
L, Derose YS, Lin YC, Bieniasz M, Eyob H _et al_. Short-form Ron promotes spontaneous breast cancer metastasis through interaction with phosphoinositide 3-kinase. _Genes Cancer_ 2011; 2:
753–762. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Wang Q, Quan H, Zhao J, Xie C, Wang L, Lou L . RON confers lapatinib resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. _Cancer
Lett_ 2013; 340: 43–50. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Eyob H, Ekiz HA, Derose YS, Waltz SE, Williams MA, Welm AL . Inhibition of ron kinase blocks conversion of micrometastases to
overt metastases by boosting antitumor immunity. _Cancer Discov_ 2013; 3: 751–760. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Eckerich C, Schulte A, Martens T, Zapf S, Westphal
M, Lamszus K . RON receptor tyrosine kinase in human gliomas: expression, function, and identification of a novel soluble splice variant. _J Neurochem_ 2009; 109: 969–980. Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Ma Q, Zhang K, Guin S, Zhou YQ, Wang MH . Deletion or insertion in the first immunoglobulin-plexin-transcription (IPT) domain differentially regulates expression
and tumorigenic activities of RON receptor Tyrosine Kinase. _Mol Cancer_ 2010; 9: 307. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Yao HP, Zhuang CM, Zhou YQ, Zeng JY, Zhang RW,
Wang MH . Oncogenic variant RON160 expression in breast cancer and its potential as a therapeutic target by small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor. _Curr Cancer Drug Targets_ 2013; 13:
686–697. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server Available at:
http://web.expasy.org/peptide_cutter/peptidecutter_references.html. * Zeng JY, Sharma S, Zhou YQ, Yao HP, Hu X, Zhang R _et al_. Synergistic activities of MET/RON inhibitor BMS-777607 and
mTOR inhibitor AZD8055 to polyploid cells derived from pancreatic cancer and cancer stem cells. _Mol Cancer Ther_ 2014; 13: 37–48. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Xu XM, Zhou YQ,
Wang MH . Mechanisms of cytoplasmic {beta}-catenin accumulation and its involvement in tumorigenic activities mediated by oncogenic splicing variant of the receptor originated from Nantes
tyrosine kinase. _J Biol Chem_ 2005; 280: 25087–25094. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Corcoran RB, Contino G, Deshpande V, Tzatsos A, Conrad C, Benes CH _et al_. STAT3 plays a
critical role in KRAS-induced pancreatic tumorigenesis. _Cancer Res_ 2011; 71: 5020–5029. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Catenacci DV, Cervantes G, Yala S, Nelson
EA, El-Hashani E, Kanteti R _et al_. RON (MST1R) is a novel prognostic marker and therapeutic target for gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma. _Cancer Biol Ther_ 2011; 12: 9–46. Article CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Thomas RM, Jaquish DV, French RP, Lowy AM . The RON tyrosine kinase receptor regulates vascular endothelial growth factor production in pancreatic
cancer cells. _Pancreas_ 2010; 39: 301–307. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Ouyang H, Mou L, Luk C, Liu N, Karaskova J, Squire J _et al_. Immortal human pancreatic
duct epithelial cell lines with near normal genotype and phenotype. _Am J Pathol_ 2000; 157: 1623–1631. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Angeloni D,
Danilkovitch-Miagkova A, Ivanov SV, Breathnach R, Johnson BE, Leonard EJ _et al_. Gene structure of the human receptor tyrosine kinase RON and mutation analysis in lung cancer samples.
_Genes Chromosomes Cancer_ 2000; 29: 147–156. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Braga E, Loginov W, Khodyrev D, Pronina I, Kazubskaya T, Bogatyrova O _et al_. A novel MECA3 region in
human 3p21.3 harboring putative tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes. _Exp Oncol_ 2011; 33: 33–41. CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kumanogoh A, Kikutani H . Immunological functions of the
neuropilins and plexins as receptors for semaphorins. _Nat Rev Immunol_ 2013; 13: 802–814. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Conrotto P, Corso S, Gamberini S, Comoglio PM, Giordano S .
Interplay between scatter factor receptors and B plexins controls invasive growth. _Oncogene_ 2004; 23: 5131–5137. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Neesse A, Michl P, Frese KK, Feig
C, Cook N, Jacobetz MA _et al_. Stromal biology and therapy in pancreatic cancer. _Gut_ 2011; 60: 861–868. Article PubMed Google Scholar * Tactacan CM, Chang DK, Cowley MJ, Humphrey ES,
Wu J, Gill AJ _et al_. RON is not a prognostic marker for resectable pancreatic cancer. _BMC Cancer_ 2012; 12: 395. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Rubio-Viqueira B,
Jimeno A, Cusatis G, Zhang X, Iacobuzio-Donahue C, Karikari C _et al_. An _in vivo_ platform for translational drug development in pancreatic cancer. _Clin Cancer Res_ 2006; 12: 4652–4661.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Kim MP, Evans DB, Wang H, Abbruzzese JL, Fleming JB, Gallick GE . Generation of orthotopic and heterotopic human pancreatic cancer xenografts in
immunodeficient mice. _Nat Protoc_ 2009; 4: 1670–1680. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Pfaffl MW Quantification strategies in real-time PCR. In: Bustin SA (ed). _A-Z
of Quantitative PCR._ International University Line (IUL): La Jolla, CA, USA, 2004, pp 87–112.. * Guttman M, Betts GN, Barnes H, Ghassemian M, van der Geer P, Komives EA . Interactions of
the NPXY microdomains of the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1. _Proteomics_ 2009; 9: 5016–5028. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * McCormack AL,
Schieltz DM, Goode B, Yang S, Barnes G, Drubin D _et al_. Direct analysis and identification of proteins in mixtures by LC/MS/MS and database searching at the low-femtomole level. _Anal
Chem_ 1997; 69: 767–776. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Furukawa T, Duguid WP, Rosenberg L, Viallet J, Galloway DA, Tsao MS . Long-term culture and immortalization of epithelial
cells from normal adult human pancreatic ducts transfected by the E6E7 gene of human papilloma virus 16. _Am J Pathol_ 1996; 148: 1763–1770. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We gratefully acknowledge the generosity of our patients who supported this work through both monetary contributions and/or by allowing tumor tissue to
be used for research. Without their contributions, this work would not have been possible. We thank the Tsao and Klemke labs for providing HPDE and HPNE ells, respectively. Research reported
in this publication was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number R01 CA155620 (AML) and T32 CA121938 (JC). The content is solely
the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. DNA sequencing was performed by the DNA Sequencing Shared
Resource, UCSD Moore’s Cancer Center, which is funded in part by NCI Cancer Center Support Grant # 2 P30 CA023100-23. AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Surgery,
Division of Surgical Oncology, Moores Cancer Center, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, CA, USA J Chakedis, R French, M Babicky, D Jaquish, H Howard, E Mose, R Lam, P Holman, J
Miyamoto, Z Walterscheid & A M Lowy Authors * J Chakedis View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * R French View author publications You can
also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M Babicky View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * D Jaquish View author publications You
can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * H Howard View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * E Mose View author publications You
can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * R Lam View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * P Holman View author publications You
can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * J Miyamoto View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Z Walterscheid View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * A M Lowy View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CORRESPONDING AUTHOR
Correspondence to A M Lowy. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no conflict of interest. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on
the Oncogene website SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (PDF 2399 KB) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Chakedis, J.,
French, R., Babicky, M. _et al._ A novel protein isoform of the RON tyrosine kinase receptor transforms human pancreatic duct epithelial cells. _Oncogene_ 35, 3249–3259 (2016).
https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.384 Download citation * Received: 14 February 2014 * Revised: 27 July 2015 * Accepted: 28 August 2015 * Published: 19 October 2015 * Issue Date: 23 June 2016
* DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.384 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not
currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative