Pentoxifylline ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat intestine• 702
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:

Intestinal ischemia/reperfusion (IR) injury often sets the stage for subsequent development of gut necrosis. Pentoxifylline (PTX) is known to be to increase RBC deformability and
prostacyclin release, both improving the microcirculation; to decrease the adhesiveness of activated PMN's, potentially reducing subsequent release of autodestructive myeloperoxidase
and superoxide radicals, and to inhibit production of cytokine mediators. We hypothesized, therefore, that PTX would be effective in ameliorating intestinal necrosis resulting from IR
injury. _METHODS_ Adult rats were anesthetized with pentobarbital; their abdomens surgically opened and intestinal vasculature exposed; and assigned to one of three groups: CONTROL(n=7)- no
further intervention; IR (n=9)- after stabilization, the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries were clamped for 45 minutes, and then perfusion was re-established; PTX (n=9)- same as IR
protocol, but animals were treated with PTX at baseline (BL), 30 and 60 min. Blood was taken for measurement of Thiobarbituric Acid Reducing Substances (TBARS), a measure of lipid
peroxidation, at BL, 45 min. (end of ischemia for latter groups), and at 60 and 75 min (15 and 30 min. of reperfusion for latter groups). At the conclusion of the experiment, intestinal
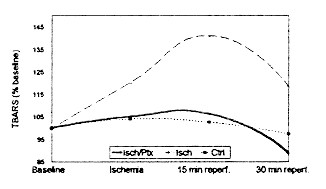
samples were removed and preserved in formalin for histological examination. Pathologic lesions were graded from 0(no lesions) to 3(severe lesions) _RESULTS_ TBARS of the three groups are
presented graphically (IR vs. both other groups; p<0.05). Pathological scores were 0±0, 2.92±0.20 and 1.17±0.52 for the control, ischemia and PTX groups respectively(p=0.0005).
_CONCLUSION_ IR injury was associated with increased lipid peroxidation and necrotic lesions in the rat intestine. PTX ameliorated both of these processes. Figure AUTHOR INFORMATION AUTHORS
AND AFFILIATIONS * Depts. Neonatology, Hebrew Univ, Hadassah Med Schl, Shaare Zedek Med Ctr, Jerusalem, Israel C Hammerman, D Goldschmidt, M S Caplan, M Kaplan, M S Schimmel, A I Eidelman
& A Hochman * Perinatal Pediatrics, Evanston Hospital, Evanston, Illinois C Hammerman, D Goldschmidt, M S Caplan, M Kaplan, M S Schimmel, A I Eidelman & A Hochman * Biochemistry, Tel
Aviv Univ., Tel Aviv, Israel C Hammerman, D Goldschmidt, M S Caplan, M Kaplan, M S Schimmel, A I Eidelman & A Hochman Authors * C Hammerman View author publications You can also search
for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * D Goldschmidt View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M S Caplan View author publications You can
also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M Kaplan View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * M S Schimmel View author publications
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * A I Eidelman View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * A Hochman View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Hammerman, C., Goldschmidt, D.,
Caplan, M. _et al._ Pentoxifylline Ameliorates Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rat Intestine• 702. _Pediatr Res_ 39 (Suppl 4), 120 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199604001-00724
Download citation * Issue Date: 01 April 1996 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199604001-00724 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this
content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative