Terahertz-driven phonon upconversion in SrTiO3
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:

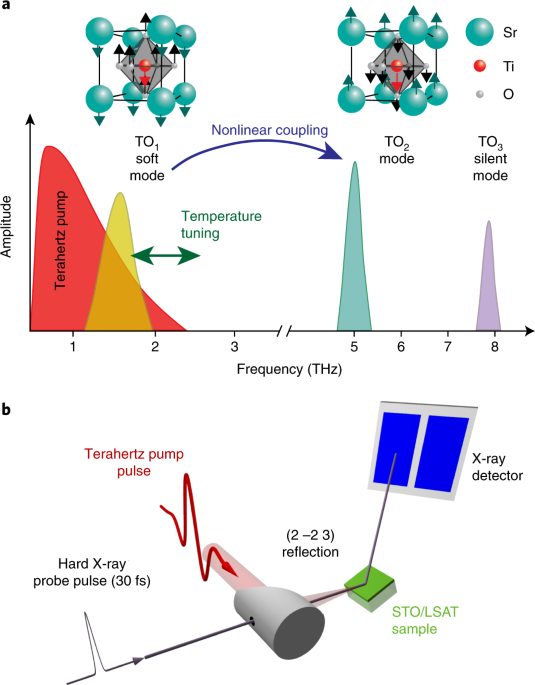
Direct manipulation of the atomic lattice using intense long-wavelength laser pulses has become a viable approach to create new states of matter in complex materials. Conventionally, a
high-frequency vibrational mode is driven resonantly by a mid-infrared laser pulse and the lattice structure is modified through indirect coupling of this infrared-active phonon to other,
lower-frequency lattice modulations. Here, we drive the lowest-frequency optical phonon in the prototypical transition metal oxide SrTiO3 well into the anharmonic regime with an intense
terahertz field. We show that it is possible to transfer energy to higher-frequency phonon modes through nonlinear coupling. Our observations are carried out by directly mapping the lattice
response to the coherent drive field with femtosecond X-ray pulses, enabling direct visualization of the atomic displacements.
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Use of the Linac Coherent Light Source, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, is supported by the US Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, under contract
no. DE-AC02-76SF00515. M.K. and M.C.H. are supported by the US Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, under award no. 2015-SLAC-100238-Funding. U.S.
acknowledges support from the National Center of Competence in Research: Ultrafast Science and Technology (NCCR MUST) of the Swiss National Science Foundation. S.B. acknowledges support from
the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation. Work at the University of Fribourg was supported by the Schweizer Nationalfonds (SNF) by grant no. 200020-172611. M.K. and M.C.H. extend thanks to
W. Chueh and A. Baclig for annealing the sample and to Z. Wu for assistance with the terahertz experiments. M.F. extends thanks to M. Först for fruitful discussions about modelling the STO
system.
Linac Coherent Light Source, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Menlo Park, CA, USA
M. Kozina, T. van Driel, J. M. Glownia, D. Zhu & M. C. Hoffmann
Max Planck Institute for the Structure and Dynamics of Matter, Hamburg, Germany
Department of Physics, University of Fribourg, Fribourg, Switzerland
Swiss Light Source, Paul Scherrer Institut, Villigen, Switzerland
Department of Physics, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden
M.K. and M.C.H. conceived the experiment and performed the final data analysis. M.F. provided DFT calculations and theory support. T.v.D. and S.B. helped with on-line data analysis. M.K.,
M.C.H., J.M.G. and D.Z. performed the time-resolved X-ray experiment. U.S. provided sample expertise and additional X-ray data. M.R. prepared the sample. P.M. and C.B. carried out the
terahertz ellipsometry measurements of the sample. The paper was written by M.K. and M.C.H., with substantial contributions from M.F., U.S. and S.B, as well as with discussions from other
authors.
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Figures 1–4, Supplementary Tables 1–5 and Supplementary References 1–3.
Animation of terahertz-driven phonon upconversion in SrTiO3.
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: