Saturated mutagenesis of ketoisovalerate decarboxylase v461 enabled specific synthesis of 1-pentanol via the ketoacid elongation cycle
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:

ABSTRACT Iterative ketoacid elongation has been an essential tool in engineering artificial metabolism, in particular the synthetic alcohols. However, precise control of product specificity
is still greatly challenged by the substrate promiscuity of the ketoacid decarboxylase, which unselectively hijacks ketoacid intermediates from the elongation cycle along with the target
ketoacid. In this work, preferential tuning of the _Lactococcus lactis_ ketoisovalerate decarboxylase (Kivd) specificity toward 1-pentanol synthesis was achieved via saturated mutagenesis of
the key residue V461 followed by screening of the resulting alcohol spectrum. Substitution of V461 with the small and polar amino acid glycine or serine significantly improved the Kivd
selectivity toward the 1-pentanol precursor 2-ketocaproate by lowering its catalytic efficiency for the upstream ketoacid 2-ketobutyrate and 2-ketovalerate. Conversely, replacing V461 with
bulky or charged side chains displayed severely adverse effect. Increasing supply of the iterative addition unit acetyl-CoA by acetate feeding further drove 2-ketoacid flux into the
elongation cycle and enhanced 1-pentanol productivity. The Kivd V461G variant enabled a 1-pentanol production specificity around 90% of the total alcohol content with or without oleyl
alcohol extraction. This work adds insight to the selectivity of Kivd active site. SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS NEW-TO-NATURE CO2-DEPENDENT ACETYL-COA ASSIMILATION ENABLED BY AN
ENGINEERED B12-DEPENDENT ACYL-COA MUTASE Article Open access 26 November 2024 RATIONAL ENGINEERING OF A THERMOSTABLE Α-OXOAMINE SYNTHASE BIOCATALYST EXPANDS THE SUBSTRATE SCOPE AND SYNTHETIC
APPLICABILITY Article Open access 13 March 2025 STRUCTURE AND MECHANISM OF A DEHYDRATASE/DECARBOXYLASE ENZYME COUPLE INVOLVED IN POLYKETIDE Β-METHYL BRANCH INCORPORATION Article Open access
18 September 2020 INTRODUCTION With genomic mining and protein engineering, biosynthesis of non-natural alcohols has made significant progress via expansion of iterative carbon chain
elongation reactions naturally found in the reverse β-oxidation1,2,3 and the branched chain amino acid pathway4,5,6. Construction of artificial metabolism has allowed production of various
aliphatic and aromatic alcohols synthetically upon enlargement of binding pocket and find-tuning of substrate specificity of key enzymes4,5,6,7. As a semi-natural metabolite, the straight
chain 1-pentanol has been detected from yeast fermentation along with other isoamyl alcohols in trace amounts8. Beyond its potential as the next generation fuel alternative with higher
energy density and lower hygroscopicity, 1-pentanol is also used industrially as coating solvent and chemical feedstock in flavor formation. While utilization of the odd-chain reverse
β-oxidation scheme resulted in a 1-pentanol titer around 0.1 g/L2, expansion of the ketoacid elongation pathway involved in leucine biosynthesis by rational design of key enzymes allowed
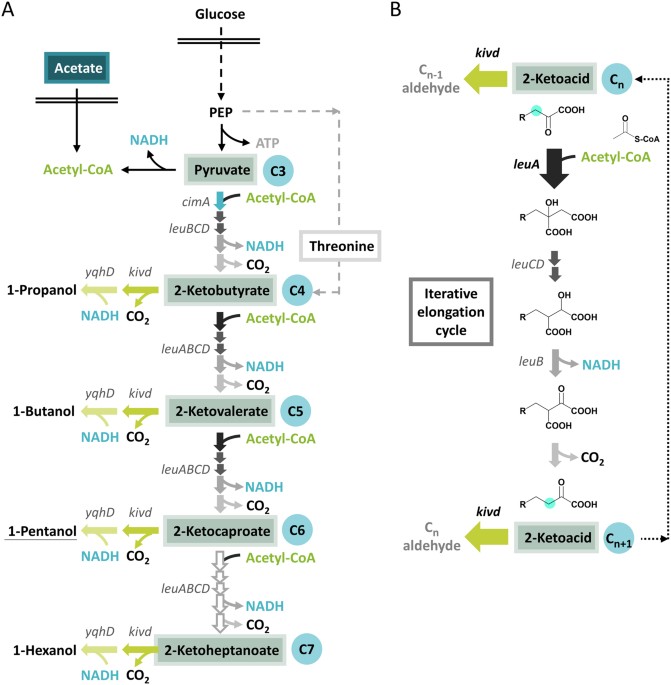
production of 0.5–2 g/L of 1-pentanol coupled to secretion of many alcohol by-products (Fig. 1A) such as the intermediate 1-propanol and 1-butanol and the downstream 1-hexanol, accounting
for a significant portion of the total alcohol content4,5,6. Although a wide variety of non-natural alcohols has been demonstrated by engineering the iterative ketoacid elongation, precise
control of product specificity is still difficult to achieve due to substrate promiscuity of the enzymes catalyzing the terminal decarboxylation and reduction reaction. Thus, it is our goal
in this work to increase the efficiency and specificity of 1-pentanol production in _Escherichia coli_ by site-saturated mutagenesis of the terminal enzyme ketoacid decarboxylase. Naturally
found in leucine biosynthesis for the extension of 2-ketoisovalerate to 2-ketoisocaproate, the enzymes encoded by _leuABCD_ catalyze the iterative elongation of 2-ketoacid using acetyl-CoA
as the recursive addition unit, inserting one carbon at the β position after each round (Fig. 1B). Aside from its native substrate, the committing enzyme 2-isopropylmalate synthase (LeuA)
was also observed to react efficiently with 2-ketobutyrate (2KB), leading to the unspecific synthesis of the non-natural amino acid norvaline9. It is interesting to note that the major
gateway to repetitive ketoacid elongation appears to be controlled by LeuA while LeuBCD displayed great plasticity4, 5. Upon subsequent protein engineering, the broadened substrate
acceptance of LeuA has allowed the generation of various synthetic 2-ketoacids and the corresponding higher chain alcohols up to C8 by coupling to the promiscuous ketoisovalerate
decarboxylase Kivd from _Lactococcus lactis_ and alcohol dehydrogenase ADH6 from _Saccharomyces cerevisiae_ 5, 6. However, the substrate promiscuity of Kivd also led to inevitable production
of the upstream alcohols by hijacking the 2-ketoacid precursors unspecifically before they re-enter the iterative elongation (Fig. 1A). Depending on the relative affinity and catalytic
activity of LeuA and Kivd toward a particular 2-ketoacid, the 2-ketoacid intermediate would either enter the fate of chain elongation or leave the elongation cycle and get converted into
alcohol (Fig. 1). Thus, synthesis of higher chain alcohol such as 1-butanol via the ketoacid pathway has always been accompanied by secretion of 1-propanol derived from its direct precursor
2-ketobutyrate10, 11. Previously, formation of the upstream alcohol byproducts could be effectively lowered by spatial separation of Kivd and the 2-ketoacid intermediates via
compartmentalization as demonstrated in _S_. _cerevisiae_ 12. On the other hand, bioprospecting and mutagenesis of Kivd homologues6 also successfully skewed the straight-chain alcohol
distribution from C3–C7 to C5–C8 by dropping the overall decarboxylation activity toward shorter 2-ketoacids. In particular, the V461A/F381L4, 5 and the G402V/M538L/F542V6 variants created
by two independent studies demonstrated the most prominent enhancement in the Kivd specificity toward higher chain 2-ketoacids and achieved the synthesis of various branched and straight
chain alcohols up to 1-octanol when coupled to LeuA mutants. While previous approaches integrating genomic mining, homology modeling, and computation-directed mutagenesis have shown great
success toward expanding the artificial alcohol repertoire, here we aim to mine the potential of the key residue V461 for its ability to fine-tune Kivd selectivity toward 2-ketocaproate by
saturated mutagenesis. By screening Kivd V461 variants, a key residue previously shown to play significant role in the 2-ketoacid preference of Kivd, we successfully minimized the diversion
of 2-ketoacid flux into intermediate alcohols 1-propanol and 1-butanol and improved the production specificity of 1-pentanol from 40% to 90% of the total alcohol content. Utilization of the
wild type LeuAFBR (feedback resistant) in the ketoacid elongation cycle also effectively suppressed the formation of downstream 1-hexanol due to its natural inefficiency to extend
2-ketocaproate further as demonstrated previously by _in vitro_ study5. Supply of the essential precursor 2KB was achieved via overexpression of the citramalate pathway coupled to native
activity of the threonine pathway synergistically. Here, saturated mutagenesis enabled us to examine the full potential of residue 461 in controlling the Kivd selectivity that may sometimes
be overlooked or difficult to pinpoint by rational design. Although laborious, screening of saturated mutants provides complete information on the impact of a single residue toward a desired
function. The positive Kivd variant V461G minimized diversion of flux into the upstream 1-propanol and 1-butanol and demonstrated superior specificity toward 1-pentanol synthesis, which was
not achieved previously with the V461A substitution4. Kinetic characterization of the positive Kivd mutants revealed that the increase in 1-pentanol specificity was a result of decreased
activity toward the upstream 2KB and 2-ketovalerate (2KV). Furthermore, external feeding of acetate to ensure adequate supply of the recursive addition unit acetyl-CoA for multiple rounds of
ketoacid elongation was confirmed beneficial toward alcohol production for the first time in this work. With _in situ_ extraction using oleyl alcohol, the final titer of 1-pentanol reached
4.3 g/L with complete abolishment of 1-propanol and 1-butanol level less than 4% of the total alcohol secreted. These strategies should be applicable to the engineering of artificial
metabolism based on the iterative ketoacid elongation. This work not only demonstrates that Kivd specificity can be directly controlled by mutation of a single residue rather than double or
tripled mutants as shown previously, but also helps building the foundation for further refining of Kivd selectivity based on the resulting alcohol spectrum of the 20 mutants. RESULTS AND
DISCUSSION INCREASING LEUA EXPRESSION TO DRIVE THE KETOACID ELONGATION CYCLE TOWARD 2-KETOCAPROATE To develop a strain which synthesizes 1-pentanol with high efficiency and specificity, we
must first ensure sufficient supply of 2KB and adequate expression of LeuA to channel carbon flux into two rounds of ketoacid elongation (Fig. 1A). As shown previously, biosynthesis of 2KB
in _E_. _coli_ can be achieved by overexpression of the native threonine pathway11 or the heterologous citramalate pathway upon evolution of the citramalate synthase (CimA) from
_Methanococcus jannaschii_ 10. Originated from their complementary nature, synergy of the threonine pathway and the citramalate pathway for 2KB synthesis was further demonstrated using
1-propanol production as a readout13, leading to higher yield and productivity of 1-propanol compared to the level obtained by each pathway individually. Therefore, overexpression of the
citramalate pathway coupled to native activity of the threonine pathway was adopted in this case to ensure efficient supply of 2KB to initiate the elongation cycle. Once entered the
elongation cycle, the relative activity of LeuA and Kivd toward each 2-ketoacid will determine the resulting alcohol spectrum. Examination of their _in vitro_ catalytic efficiencies revealed
that whereas wild type (WT) Kivd exhibits broad activity toward C4–C8 straight chain 2-ketoacids6, WT LeuAFBR (feedback resistant variant G462D) displayed significant drop in activity
starting at the C6 2-ketocaproate (2KC)5. The intrinsic limitation of WT leuAFBR to extend 2KC further therefore is taken advantage of to terminate the ketoacid elongation cycle at the
1-pentanol stage. The NADPH-dependent aldehyde reductase encoded by _yqhD_ from _E_. _coli_ was used here toward alcohol production for its high solubility and broad substrate range
demonstrated previously by various studies14,15,16,17,18. Since the competition between LeuA and Kivd decides the fate of the intermediate 2-ketoacids (Fig. 1), we first set out to increase
the expression of LeuA in the hope to enhance the rate of ketoacid elongation and lower the formation of upstream alcohol byproducts. Compared to the previous construct where LeuA was
overexpressed from a medium copy plasmid behind CimA* (pSA142)10, here we cloned the feedback resistant LeuAFBR (G462D) as the first gene downstream of PLlacO1 on a high copy plasmid (pGC3).
Enzymes CimA* and the promiscuous LeuBCD remained overexpressed from the medium copy plasmid pAFC52. It is noted that the CimA* mutant Δ210 was used in this study for its similar
performance but less amino acid substitution compared to the mutant 3.7 harbored on plasmid pSA142. Since the primary focus of this study was to improve the specificity of straight chain
alcohols synthesized via the elongation cycle by tuning Kivd selectivity for a particular chain length, the branched chain amino acid (BCAA) pathways were disrupted by the elimination of
acetohydroxy acid synthase I and III encoded by _ilvB_ and _ilvI_. Studies focusing on straight chain alcohols5, 6 have consistently taken this approach to completely abolish synthesis of
methyl alcohols for better readout of Kivd activity toward straight chain 2-ketoacids. Strain CRS59 (Δ_ilvB_ Δ_ilvI_ Δ_leuA_) therefore was used here to eliminate competition of key enzymes
and precursors by the BCAA pathway and to minimize background effect from the chromosomal _leuA_. During the design of synthetic operon on plasmid pGC3 (Table 1), we noticed the presence of
a potential ribosomal binding site (RBS) embedded at the end of _leuA_ coding region which originally drives the expression of _leuB_ in _E_. _coli_’s native _leuABCD_ operon. Since it was
unclear whether _kivd_ could be sufficiently expressed following _leuA_ using this native RBS (Fig. 2, pGC3), we also cloned an alternative construct (Fig. 2, pGC4) with additional insertion
of a strong RBS in front of kivd and compared their effect on alcohol production. As shown on Fig. 2, increasing expression of LeuAFBR on plasmid pGC3 effectively enhanced the relative
ratio of 1-pentanol from 1% to about 40% of the total alcohol content, with an overall increase in the 1-butanol and 1-pentanol titer to 1.1 g/L and 1.0 g/L respectively in 48 h. 1-Propanol
production, on the other hand, reduced by 85% to 0.4 g/L, indicating the enhanced channeling of 2KB into the ketoacid elongation cycle. Minimal level of 1-hexanol detected in the culture
broth confirmed the cessation of ketoacid elongation at 2KC by WT LeuA. Overall, modification of the operon structure and copy number of key enzymes not only improved the 1-pentanol
specificity, but also raised the total alcohol titer downstream of 2KB by almost three-fold, demonstrating the increased efficiency of 2-ketoacid elongation. On the other hand, existence of
two RBS in tandem appeared to cause detrimental effect on Kivd expression from plasmid pGC4 as reflected by the overall drop in alcohol production. These observations suggested the
sufficient expression of _kivd_ by the native _leuB_ RBS in _E_. _coli_ and the adversity of tandem RBS for translation when placed within proximity of 10 base pairs. SCREENING OF KIVD V461
VARIANTS FOR INCREASED SPECIFICITY TOWARD 2-KETOCAPROATE Previously, several key residues delineating the Kivd active site were identified to play essential role in controlling the pocket
size and acceptance of bulkier substrates, in particular F381, G402, V461, M538, and F5424, 6, 19, 20. Of all the Kivd variants examined for substrate specificity, V461 has been a common
target selected by different studies based on the homology models and molecular simulation4, 19, 20. Site-directed mutagenesis of V461 to a smaller side chain alanine or a bulkier surrogate
isoleucine resulted in respective shift in the substrate preference of Kivd according to pocket restriction by the different side chain. It was observed that replacing V461 with isoleucine
significantly lowered the Kivd catalytic efficiency toward phenylpyruvate19 while substitution of V461 with alanine increased the Kivd specificity toward longer 2-ketoacids4. To fully
explore the potential of residue 461 in controlling the substrate specificity of Kivd, we performed saturated mutagenesis of V461 and screen for increased 1-pentanol production efficiency
and/or specificity. Each Kivd mutant was constructed using splicing by overlap extension (SOE) with particular codons selected based on similar frequency (~20%) as the original valine codon
in the WT. Strain CRS59 (Δ_ilvB_ Δ_ilvI_ Δ_leuA_) transformed with pAFC52 and the plasmid harboring the individual Kivd variant was used in the screening process. As shown on Fig. 3, a
unique pattern of alcohol distribution can be derived by grouping the resulting production profile based on the polarity of each amino acid residue substituted at V461. Significant drop of
straight chain alcohols to nearly non-detectable level was observed from Kivd variants containing charged side chains at the 461 position, which seemed to be independent of the side chain
length. As shown by the homology model on Fig. 4, presence of charged side chains at residue 461 might have caused undesirable repulsion with the hydrophobic alkyl group on the 2-ketoacids
and led to troubled entrance of the substrate. On the other hand, V461 substitution with polar but uncharged residues appeared to have much less dramatic impact on the Kivd decarboxylation
activity of C4–C6 2-ketoacids as shown by the decent alcohol production. In addition to the charged residues, replacing V461 with bulky side chains consisting of aromatic rings or cyclic
structure also displayed severely adverse effect on the overall alcohol production, with the lowest and highest titer observed from V461P and V461F respectively. Presence of bulky residues
at position 461 might have led to reduced pocket size and restricted entrance which hindered substrate binding. As suggested by previous modeling of the Kivd active site20, hydrophobic
interactions between the alkyl group on the 2-ketoacids and the key residues helped secure the substrate in the binding pocket. Furthermore, the substrate channel and pocket size of Kivd is
restricted by the residues F542, M538, I465 and V461. These observations may help explain the significant drop in Kivd activity when V461 was replaced with charged and/or bulky residues,
which possibly impaired the hydrophobic interaction and further shrunk the binding pocket respectively. As shown by Fig. 4, the modeled distance between the methyl group on pyruvate and the
side chain on amino acid 461 decreased dramatically in the presence of bulky residues, indicating the potential steric clash with 2-ketoacid substrates. It is noted that the original
hydrogen bonding between residue 461/465 and residue 461/cofactor TPP remains unchanged by the V461 substitutions in the homology model. Nearly all of the successful V461 substitutions which
maintained similar alcohol production efficiency and improved 1-pentanol specificity have relatively small aliphatic side chains compared to the structure of valine present in the WT, with
three winners belonging in the polar group (V461S, V461C, V461G) and two winners found in the nonpolar group (V461A, V461M). Except for the case of methionine which consists of four atoms in
the side chain, serine, cysteine, glycine and alanine are all short amino acids with one to two atoms in the side chain. The extra space created in the binding pocket of Kivd by these
smaller amino acid substitutions might have caused loose or unstable docking of the shorter substrates 2KB and 2KV thus allowing higher specificity toward 2KC for 1-pentanol synthesis. In
particular, replacing V461 with glycine resulted in the greatest distance between the methyl group on pyruvate and the side chain on residue 461, which led to the most significant
improvement in the Kivd selectivity toward 2KC as shown later in the kinetic assay. It is noted that substitutions which increased 1-pentanol specificity but significantly lowered its titer,
such as V461N, V461Q, V461E, and V461F, were not carried forward in this study. At the end, the best-performing Kivd variants V461S and V461G were selected from the five winners for their
minimal level of 1-propanol and 1-butanol produced and were moved onto further kinetic characterization. SUBSTITUTION V461G AND V461S DRAMATICALLY LOWERED KIVD CATALYTIC EFFICIENCY TOWARD
2-KETOBUTYRATE AND 2-KETOVALERATE To analyze how the Kivd V461S and V461G mutants enabled significant increase in 1-pentanol production specificity, we set out to characterize their _k_
_cat_ and _K_ _m_ toward each 2-ketoacid (2KB, 2KV, and 2KC) in the elongation cycle using purified protein and compared the resulting level to that of the WT Kivd. Kinetic characterization
of Kivd WT and mutants toward the natural substrate 2-ketoisovalerate (2KIV) was also performed to examine the effect of V461S and V461G on its catalytic efficiency for branched chain
substrates. The Kivd variant V461S, V461G, and WT Kivd were re-cloned with 6X-His tag attached to the N-terminus and purified. As shown on Table 2, replacing V461 with the small and polar
residue glycine and serine dramatically lowered the catalytic efficiency (_k_ _cat_ /_K_ _m_ ) of Kivd toward 2KB and 2KV by 80–95% while retaining 60–90% of its original activity toward
2KC. In the case of V461G, the enhancement of 2KC specificity was majorly attributed to the decrease in _k_ _cat_ for 2KB and increase in _K_ _m_ for 2KV; on the other hand, the reversed
phenomenon was observed in the case of V461S (decrease in _k_ _cat_ for 2KV and increase in _K_ _m_ for 2KB). Whereas the V461G variant demonstrated higher activity drop for 2KV, the V461S
variant displayed greater activity drop for 2KB. In contrast to previous Kivd mutants V461A/F381L4 and G402V/M538L/F542V6 where increased specificity was coupled to significant decrease in
the catalytic efficiency toward the target C7 2-keto-4-methylhexanoate and the C8 2-ketooctanoate respectively, in this case the V461S and V461G substitution only led to a 10–40% drop in the
Kivd activity toward 2KC with slightly lowered _k_ _cat_ and decreased _K_ _m_ . It is interesting to note that both mutants displayed about 90% drop in the catalytic efficiency toward the
natural substrate 2KIV, suggesting their potential application in engineering specificity for products deriving from the branched-chain 2-ketoacids. Here, the significant reduction of Kivd
activity for 2KB and 2KV by the V461G and V461S substitution allowed LeuA to pull the 2-ketoacid flux into the elongation cycle more effectively, thus increased the 1-pentanol specificity to
about 90% of the total alcohol content despite the small concurrent drop of Kivd activity toward 2KC. This work also demonstrates that mutation of a single residue was able to directly tune
the specificity of Kivd which previously required a combination of double or triple mutants. FEEDING OF ACETATE ENHANCED SUPPLY OF THE ITERATIVE ADDITION UNIT AND INCREASED 1-PENTANOL
PRODUCTION As shown by Fig. 1A, biosynthesis of 1-pentanol via the 2-ketoacid pathway demands high level of acetyl-CoA as the repetitive addition unit. One molecule of acetyl-CoA is consumed
to extend the 2-ketoacid by one carbon in every round of the elongation cycle. Production of one molecule of 1-pentanol therefore requires three molecules of acetyl-CoA to elongate the C3
pyruvate into the C6 2KC, leading to the maximum theoretical yield of 0.5 mole 1-pentanol per mole of glucose (0.24 g/g glucose). To examine if 1-pentanol synthesis is limited by the
acetyl-CoA flux, we attempted feeding of various level of acetate at different time interval to the production culture and measured the resulting alcohol accumulation. Strain Δ_ilvB_ Δ_ilvI_
Δ_leuA_ transformed with pAFC52 and another plasmid harboring the individual Kivd variant V461S, V461G, V461A or WT Kivd was used in this study. Feeding of acetate to the production culture
of WT Kivd and the well-characterized V461A mutant was performed to see if increased supply of acetyl-CoA alone could skew the alcohol distribution toward 1-pentanol. As shown on Fig. 5,
extracellular feeding of 5 g/L acetate at induction led to the most consistent improvement in 1-pentanol production from the Kivd mutant V461S and V461G, increasing the 1-pentanol titer by
nearly two-fold to 2.2 g/L in 48 h. It is noted that feeding of acetate could potentially push the 1-pentanol yield above the maximum theoretical level; however, in our case the highest
yield of 1-pentanol only reached about 0.12 g/g glucose. Production of 1-butanol and 1-propanol remained below 5% of the total alcohol content, indicating the efficient pulling of 2-ketoacid
into the elongation cycle under enhanced supply of acetyl-CoA. On the other hand, when WT Kivd was used, elevating acetyl-CoA supply led to greater improvement in 1-butanol production (80%
increase) compared to 1-pentanol (0–30% increase), thus dropping the overall 1-pentanol specificity even further. In the case of the V461A mutant, additional feeding of acetate increased the
production of 1-pentanol quite significantly but was unable to boost the specificity much further due to the concurrent increase in 1-butanol synthesis. Combined with the observations
above, these results demonstrate that while enhancing acetyl-CoA flux helps driving 2-ketoacids into the elongation cycle, Kivd specificity still plays a much more dominant role in
determining the resulting alcohol spectrum. Our attempt to prolong and further elevate the 1-pentanol production by pH adjustment and increasing culture density was not successful. Synthesis
of 1-pentanol plateaued around 2.5 g/L (Fig. 6A) despite maintenance of neutral pH, intermittent supply of acetate, and increasing concentration of yeast extract (Supplementary Figure S2A).
Here, the level of yeast extract supplemented to the medium was raised above 5 g/L in the hope to sustain 1-pentanol synthesis by enhancing cellular growth and repair via increased amino
acid supply. Raising the yeast extract concentration from 5 g/L to 20 g/L led to higher biomass accumulation and boosted the 1-pentanol productivity by two-fold (Supplementary Figure S2A);
however, 1-pentanol yield decreased from 0.12 g/g to 0.07 g/g due to significant diversion of carbon flux into biomass. Although increasing nutrient supply doubled the production rate, it
still failed to push the 1-pentanol titer beyond 2.5 g/L. These observations led us to hypothesize that 1-pentanol toxicity, which was shown to be more severe than 1-butanol and cause growth
hindrance at 1 g/L6, contributes significantly to the cessation of 1-pentanol production here. _IN SITU_ EXTRACTION USING OLEYL ALCOHOL PUSHED 1-PENTANOL TITER FURTHER With good
biocompatibility and low bioavailability as a microbial carbon source21, oleyl alcohol has been commonly used in two-phase systems to continuously remove product from the fermentation
culture22. The effectiveness of oleyl alcohol for _in situ_ extraction to minimize end-product accumulation and lower the toxicity effect has been successfully demonstrated for the
production of many C4 and C5 alcohols such as 1-butanol23,24,25, isobutanol26, and 3-methyl-1-butanol27. To examine if continuous extraction of 1-pentanol would help improve the titer above
2.5 g/L, we performed two-phase production tests with equal volume of liquid culture and oleyl alcohol (10 mL each). Kivd mutant V461G was used here for its better performance in the
1-pentanol production specificity with overall lower catalytic efficiency toward 2KB and 2KV. Oleyl alcohol was added to the culture medium at inoculation to allow immediate extraction of
the alcohols produced. As shown on Fig. 6B, presence of oleyl alcohol was only able to extend the 1-pentanol production period slightly, reaching a titer of 4.3 g/L in 149 h with higher
variation toward the later production phase. Affinity of alcohols for the oil layer increased with their hydrophobicity; nearly 95% and 100% of the 1-pentanol and 1-hexanol produced
respectively partitioned into the oil phase. Interestingly, continuous oil extraction led to a slight decrease in the secretion of the upstream byproduct 1-butanol and slight increase of the
downstream byproduct 1-hexanol, thus maintaining the 1-pentanol specificity at around 90%. Also, the addition of oleyl alcohol appeared to have a bit of detrimental effect on the alcohol
productivity and cell viability, causing the 1-pentanol production rate to drop by 40% upon exposure to the oil phase compared to the level obtained without oil extraction. Similar
phenomenon was also observed in the two-phase fermentation of 3-methyl-1-butanol27 and might be caused by the decrease in culture aerobicity upon mixing with the oil layer in screwed cap
flasks. Significantly higher productivity of 1-pentanol was achieved using TB medium (Supplementary Figure S2B), although it was coupled to lower yield as a result of carbon diversion into
biomass. Despite the increased production rate, 1-pentanol synthesis under the highly nutritious TB plateaued at around 4 g/L in 48 h. In all cases, we observed a positive correlation
between acetate usage and 1-pentanol production; the plateau of 1-pentanol synthesis was consistently coupled to the cessation of acetate consumption. Here, _in situ_ extraction using oleyl
alcohol slightly prolonged the 1-pentanol production but was unable to resolve its intrinsic pathway inefficiency as reflected by its sluggish productivity. It is noted that straight chain
alcohols such as 1-pentanol and 1-hexanol were shown to induce great alteration to membrane fluidity and cellular physiology due to their deep penetration into the phospholipid
structure28,29,30. In this case, continuous removal of the alcohol products may help lower the toxicity but the potential metabolic imbalance and irreversible membrane disruption caused by
1-pentanol synthesis remained as an issue. In conclusion, saturated mutagenesis of a single Kivd residue effectively improved 1-pentanol production specificity; however, production
efficiency of 1-pentanol is still challenged by its toxicity and the pathway bottleneck possibly induced by the accumulation of inhibitory metabolites. MATERIALS AND METHODS REAGENTS AND
CHEMICALS All chemicals and reagents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis, MO) or Thermo Scientific (Pittsburgh, PA) unless specified otherwise. KOD DNA polymerase was purchased
from EMD Chemicals (San Diego, CA). Taq DNA ligase, Phusion High-Fidelity DNA polymerase, and T5 exonuclease were obtained from New England Biolabs (Ipswich, MA). Oligonucleotides were
purchased from IDT (San Diego, CA). BACTERIAL STRAINS _Escherichia coli_ BW25113 (_rrnB_ T14 ∆_lacZ_ WJ16 _hsdR514_ ∆_araBAD_ AH33 ∆_rhaBAD_ LD78) was designated as the wild-type (WT)31.
XL-1 Blue (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) was used to propagate all plasmids. Construction of the strain CRS59 (BW25113 with _lacI_ _q_ provided on F’ with ∆_ilvB_ ∆_ilvI_ ∆_leuA_) was described
previously13. PLASMID CONSTRUCTION All plasmids were created by the Gibson isothermal DNA assembly method32 using purified PCR fragments. A list of primers is shown on the Supplementary
Table S1 and the plasmids used is shown on Table 1. It is noted that a strong RBS (AGGAGATATACC) was used to drive every gene in the synthetic operon except for _kivd_ expression from
pGC13-pGC33 where the native _E_. _coli_ RBS for _leuB_ was used (embedded at the end of _leuA_, about 10 bp away from the stop codon). To create pGC3, the vector backbone (ColE1 ori, Ampr)
and the operon _kivd_-_yqhD_ were amplified from plasmid pSA13818 using primers GC1/GC2 and GC4/GC6 respectively while the feedback resistant _leuA_ FBR (G462D) was amplified from plasmid
pCS125 (unpublished) with primers GC3/GC5. The resulting PCR products were gel-purified and assembled together. It is noted that in the case of pGC3, the native _leuB_ RBS embedded at the
end of _leuA_ was used to drive _kivd_ expression and no synthetic RBS was inserted in front of _kivd_. To create pGC4, the operon _kivd_-_yqhD_ was amplified using primers GC4/GC8 and the
_leuA_ FBR (G462D) was amplified using GC3/GC7. The resulting PCR products were gel-purified and assembled with the same vector backbone amplified using GC1/GC2. To create the 19 Kivd
variants with saturated mutation of the V461 residue, we designed primers carrying the specific mutation (GC47, 48, 53–88) and amplified the _kivd_*-_yqhD_ fragment with GC4 and GC6 coupling
to primers GC47-GC88 for the distinct mutation. The list of primers can be found in the Supplementary Table S1 where underline indicates the specific mutation introduced. The resulting PCR
products were gel-purified and assembled with the _leuA_ (G462D) fragment and the vector backbone using identical procedure. The plasmids were then sequenced to confirm the introduction of
specific mutation. To create pCSGC1–3, the specific _kivd_ variant was amplified using primers SW19/20 and assembled to the vector backbone amplified using primers SW21/22 from pCS180
(unpublished). PRODUCTION MEDIUM AND PROCEDURE For all of the alcohol production experiments, single colonies were picked from LB (Luria Broth) plates and inoculated into 2 mL of LB medium
contained in test tubes with the appropriate antibiotics (tetracycline 15 μg/mL, ampicillin 100 μg/mL, kanamycin 50 μg/mL). Unless otherwise specified, the overnight culture grown at 37 °C
was inoculated 1% (v/v) into 15 mL of M9 medium (12.8 g/L Na2HPO4·7H2O, 3 g/L KH2PO4, 0.5 g/L NaCl, 1 g/L NH4Cl, 1 mM MgSO4, 1 mg/L vitamin B1 and 0.1 mM CaCl2) containing 30 g/L of glucose,
5 g/L of yeast extract (BD Bacto, Franklin Lakes, NJ), 1000X Trace Metal Mix A5 (2.86 g H3BO3, 1.81 g MnCl2·4H2O, 0.222 g ZnSO4·7H2O, 0.39 g Na2MoO4·2H2O, 0.079 g CuSO4·5H2O, 0.049 g
Co(NO3)2·6H2O per liter water) and appropriate antibiotics in 250 mL screwed-cap flasks. The culture was allowed to grow at 37 °C in a rotary shaker (250 rpm) to an OD600 of 0.6–0.8 then
induced with 0.1 mM IPTG and moved to 30 °C for alcohol production. Samples were taken throughout the next few days and culture broths were centrifuged and filtered to retrieve the
supernatant. Identical procedure as described above was used in the alcohol screening experiment of the 20 different Kivd variant. Whenever feeding of acetate was performed, specified amount
of sodium acetate was externally added to the production culture at induction and at various time points during the long-term production as indicated in the text. For long-term alcohol
productions lasting more than 48 h, 30 g/L of glucose was supplied initially in the production medium. Terrific Broth (12 g tryptone, 24 g yeast extract, 2.31 g KH2PO4, 12.54 g K2HPO4, 4 mL
glycerol per liter of water) was also tested as a comparison. Culture pH was adjusted to 7 using 10 M NaOH every day to maintain the pH above 6.6. Additional glucose was fed at the 48 h to
maintain the glucose level above 10 g/L. For the production experiments with oleyl alcohol extraction, identical procedure was used except equal volume (10 mL) of oleyl alcohol was added to
the culture medium (10 mL) at inoculation. Samples were taken from both the oil and aqueous layer in equal volume upon separation of the two phases. QUANTIFICATION OF METABOLITES Samples
were centrifuged or filtered to gather the supernatant for GC and HPLC analysis. The amount of alcohol produced was quantified by gas chromatograph (GC) equipped with a flame ionization
detector (FID). The system is a Shimadzu GC-2010 plus with an AOC-20i auto-injector and an AOC-20s auto-sampler. The separation of alcohol compounds was performed by HP-Chiral-20B column (30
m, 0.32 mm i.d., 0.25 μm film thickness) purchased from Agilent. GC oven temperature was initially held at 60 °C for 2 min and raised with a gradient of 10 °C/min until 85 °C and held for 2
min. And then it was raised with a gradient of 45 °C/min until 230 °C and held for 1 min. Helium was used as the carrier gas. The injector was maintained at 225 °C and the detector was
maintained at 235 °C. The supernatant (1 μL) of culture broth was injected in split injection mode (1:15 split ratio) using isobutanol as the internal standard. For oleyl alcohol samples,
identical procedure was used except samples were diluted with HPLC grade hexane to reduce the viscosity for injection accuracy. To measure concentration of glucose and organic acids,
filtered supernatant was applied to an Agilent 1260 HPLC equipped with an auto-sampler and an Agilent Hi-Plex H column (5 mM H2SO4, 0.6 mL/min, column temperature at 50 °C). Glucose was
measured with refractive index detector while organic acids were detected using a photodiode array detector at 210 nm. PURIFICATION AND _IN VITRO_ ASSAY OF KIVD Protein purification was done
using the His-Spin Protein Miniprep Purification kit from Zymo Research (Irvine, CA). Overnight culture of the XL-1 strain harboring the target Kivd mutant (V461G and V461S) and the wild
type Kivd was individually used to inoculate 20 mL of fresh LB with appropriate antibiotics. The culture was then incubated at 37 °C until exponential phase and induced with 0.1 mM IPTG. The
induced culture was incubated at 30 °C for 18–24 h to allow protein expression. The overnight culture was then harvested by centrifugation and the resulting pellet was resuspended with 1 mL
of binding buffer supplied in the kit. The resuspended culture was mixed with 1 mL of 0.1 mm glass beads (Biospec) and homogenated using a mini bead beater (Biospec). The soluble fraction
was collected by taking the clear broth after centrifugation at 4 °C. The supernatant was run through the His-binding column, washed and eluted with buffer according to the Zymo protocol.
The purified protein was collected after His-spin column purification and then mixed with glycerol for −80 °C storage. The protein concentration was determined by Bradford reagent using BSA
as standards. The _k_ _cat_ and _K_ _m_ of WT Kivd and the selected variants were measured for substrates 2KB, 2KV, 2KC, and 2KIV at 30 °C via a coupled assay using excess alcohol
dehydrogenase (ADH) from yeast (Sigma-Aldrich A7011). The decrease of absorption at 340 nm, corresponding to the consumption of NADH, was monitored for 30 min in a 96-well plate using the
Biotek Epoch 2 microplate spectrophotometer. All ketoacid substrates were dissolved in MilliQ water. Activity was measured using 1–60 mM of 2-ketoacids with the reaction mixture containing
0.5 mM NADH, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 0.2 mM TPP, 1 mM MgSO4, and 100 or 500 U/mL of ADH in 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer at pH 7.4. 500 U/mL of ADH was used for all 2-ketoacids with
concentration greater than 10 mM and for all reactions in the case of 2KIV. The reaction was initiated by the addition of the purified Kivd protein. A range of Kivd concentrations (30 nM to
1200 nM) was used to achieve steady state kinetics depending on the activity of each enzyme toward different 2-ketoacids. The values of _k_ _cat_ and _K_ _m_ were determined by fitting the
initial velocity data (averaged from 2–3 repeats) to the Michaelis-Menten equation using the software Origin. The standard deviation shown on Table 2 represents error from the non-linear
fitting. DATA AVAILABILITY The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. REFERENCES * Dekishima, Y., Lan,
E. I., Shen, C. R., Cho, K. M. & Liao, J. C. Extending carbon chain length of 1-butanol pathway for 1-hexanol synthesis from glucose by engineered _Escherichia coli_. _Journal of the
American Chemical Society_ 133, 11399–11401 (2011). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Tseng, H. C. & Prather, K. L. Controlled biosynthesis of odd-chain fuels and chemicals via
engineered modular metabolic pathways. _Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America_ 109, 17925–17930 (2012). Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central
Google Scholar * Dellomonaco, C., Clomburg, J. M., Miller, E. N. & Gonzalez, R. Engineered reversal of the beta-oxidation cycle for the synthesis of fuels and chemicals. _Nature_ 476,
355–U131 (2011). Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Zhang, K., Sawaya, M. R., Eisenberg, D. S. & Liao, J. C. Expanding metabolism for biosynthesis of nonnatural alcohols.
_Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America_ 105, 20653–20658 (2008). Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Marcheschi, R. J. _et
al_. A synthetic recursive “+1” pathway for carbon chain elongation. _ACS chemical biology_ 7, 689–697 (2012). Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Mak, W. S. _et al_.
Integrative genomic mining for enzyme function to enable engineering of a non-natural biosynthetic pathway (vol 6, 10005, 2015). _Nat Commun_ 7 (2016). * Machado, H. B., Dekishima, Y., Luo,
H., Lan, E. I. & Liao, J. C. A selection platform for carbon chain elongation using the CoA-dependent pathway to produce linear higher alcohols. _Metab Eng_ 14, 504–511 (2012). Article
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Cann, A. F. & Liao, J. C. Pentanol isomer synthesis in engineered microorganisms. _Appl Microbiol Biot_ 85, 893–899 (2010). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Soini, J. _et al_. Norvaline is accumulated after a down-shift of oxygen in _Escherichia coli_ W3110. _Microb Cell Fact_ 7 (2008). * Atsumi, S. & Liao, J. C. Directed Evolution of
Methanococcus jannaschii Citramalate Synthase for Biosynthesis of 1-Propanol and 1-Butanol by _Escherichia coli_. _Appl Environ Microb_ 74, 7802–7808 (2008). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Shen, C. R. & Liao, J. C. Metabolic engineering of _Escherichia coli_ for 1-butanol and 1-propanol production via the keto-acid pathways. _Metab Eng_ 10, 312–320 (2008). Article CAS
PubMed Google Scholar * Shi, S. B. _et al_. Metabolic engineering of a synergistic pathway for n-butanol production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. _Sci Rep-Uk_ 6 (2016). * Shen, C. R. &
Liao, J. C. Synergy as design principle for metabolic engineering of 1-propanol production in _Escherichia coli_. _Metab Eng_ 17, 12–22 (2013). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Perez,
J. M., Arenas, F. A., Pradenas, G. A., Sandoval, J. M. & Vasquez, C. C. _Escherichia coli_ YqhD exhibits aldehyde reductase activity and protects from the harmful effect of lipid
peroxidation-derived aldehydes. _J Biol Chem_ 283, 7346–7353 (2008). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Koma, D., Yamanaka, H., Moriyoshi, K., Ohmoto, T. & Sakai, K. Production of
Aromatic Compounds by Metabolically Engineered _Escherichia coli_ with an Expanded Shikimate Pathway. _Appl Environ Microb_ 78, 6203–6216 (2012). Article CAS Google Scholar * Alkim, C.
_et al_. Optimization of ethylene glycol production from (D)-xylose via a synthetic pathway implemented in _Escherichia coli_. _Microb Cell Fact_ 14 (2015). * Valdehuesa, K. N. G. _et al_.
Identification of aldehyde reductase catalyzing the terminal step for conversion of xylose to butanetriol in engineered _Escherichia coli_. _Bioproc Biosyst Eng_ 38, 1761–1772 (2015).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Atsumi, S. _et al_. Engineering the isobutanol biosynthetic pathway in _Escherichia coli_ by comparison of three aldehyde reductase/alcohol dehydrogenase
genes. _Appl Microbiol Biot_ 85, 651–657 (2010). Article CAS Google Scholar * Yep, A., Kenyon, G. L. & McLeish, M. J. Determinants of substrate specificity in KdcA, a thiamin
diphosphate-dependent decarboxylase. _Bioorg Chem_ 34, 325–336 (2006). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Berthold, C. L. _et al_. Structure of the branched-chain keto acid
decarboxylase (KdcA) from Lactococcus lactis provides insights into the structural basis for the chemoselective and enantioselective carboligation reaction. _Acta Crystallogr D_ 63,
1217–1224 (2007). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Anvari, M. & Khayati, G. _In situ_ recovery of 2,3-butanediol from fermentation by liquid-liquid extraction. _J Ind Microbiol
Biot_ 36, 313–317 (2009). Article CAS Google Scholar * Schugerl, K. Integrated processing of biotechnology products. _Biotechnol Adv_ 18, 581–599 (2000). Article CAS PubMed Google
Scholar * Zheng, Y. N. _et al_. Problems with the microbial production of butanol. _J Ind Microbiol Biot_ 36, 1127–1138 (2009). Article ADS CAS Google Scholar * Ezeji, T., Milne, C.,
Price, N. D. & Blaschek, H. P. Achievements and perspectives to overcome the poor solvent resistance in acetone and butanol-producing microorganisms. _Appl Microbiol Biot_ 85, 1697–1712
(2010). Article CAS Google Scholar * Lee, S. Y. _et al_. Fermentative butanol production by clostridia. _Biotechnol Bioeng_ 101, 209–228 (2008). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar *
Varman, A. M., Xiao, Y., Pakrasi, H. B. & Tang, Y. J. J. Metabolic Engineering of Synechocystis sp Strain PCC 6803 for Isobutanol Production. _Appl Environ Microb_ 79, 908–914 (2013).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Connor, M. R., Cann, A. F. & Liao, J. C. 3-Methyl-1-butanol production in _Escherichia coli_: random mutagenesis and two-phase fermentation. _Appl
Microbiol Biot_ 86, 1155–1164 (2010). Article CAS Google Scholar * Kabelitz, N., Santos, P. M. & Heipieper, H. J. Effect of aliphatic alcohols on growth and degree of saturation of
membrane lipids in Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. _FEMS microbiology letters_ 220, 223–227 (2003). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Fujita, K., Matsuyama, A., Kobayashi, Y. &
Iwahashi, H. Comprehensive gene expression analysis of the response to straight-chain alcohols in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using cDNA microarray. _J Appl Microbiol_ 97, 57–67 (2004). Article
CAS PubMed Google Scholar * Ingram, L. O. Adaptation of membrane lipids to alcohols. _Journal of bacteriology_ 125, 670–678 (1976). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar *
Datsenko, K. A. & Wanner, B. L. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in _Escherichia coli_ K-12 using PCR products. _Proc Natl Acad Sci USA_ 97, 6640–6645 (2000). Article ADS CAS
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar * Gibson, D. G. _et al_. Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. _Nat Meth_ 6, 343–345 (2009). Article CAS Google
Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology (Taiwan) with grant 105-2622-8-007-009. AUTHOR INFORMATION Author notes * Grey
S. Chen and Siang Wun Siao contributed equally to this work. AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Chemical Engineering, National Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan Grey S. Chen,
Siang Wun Siao & Claire R. Shen Authors * Grey S. Chen View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Siang Wun Siao View author publications You
can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Claire R. Shen View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS C.R.S. designed
the experiments. G.S.C. and S.W.S. performed the experiments. C.R.S., G.S.C., and S.W.S. analyzed the data. C.R.S. supervised the experiments. C.R.S. wrote the manuscript. All authors read
and approved of the final manuscript. CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Claire R. Shen. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare that they have no competing
interests. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION PUBLISHER'S NOTE: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. ELECTRONIC
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS OPEN ACCESS This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits
use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the
Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated
otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds
the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. Reprints and
permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Chen, G.S., Siao, S.W. & Shen, C.R. Saturated mutagenesis of ketoisovalerate decarboxylase V461 enabled specific synthesis of 1-pentanol
via the ketoacid elongation cycle. _Sci Rep_ 7, 11284 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11624-z Download citation * Received: 27 June 2017 * Accepted: 25 August 2017 * Published: 12
September 2017 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11624-z SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a
shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative