Role of deficient type iii interferon-λ production in asthma exacerbations
- Select a language for the TTS:
- UK English Female
- UK English Male
- US English Female
- US English Male
- Australian Female
- Australian Male
- Language selected: (auto detect) - EN
Play all audios:

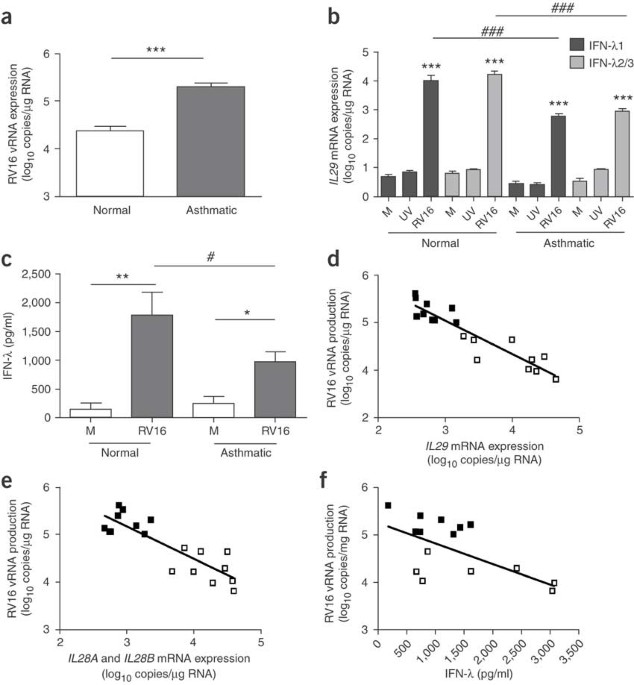
ABSTRACT Rhinoviruses are the major cause of asthma exacerbations, and asthmatics have increased susceptibility to rhinovirus and risk of invasive bacterial infections. Here we show
deficient induction of interferon-λs by rhinovirus in asthmatic primary bronchial epithelial cells and alveolar macrophages, which was highly correlated with severity of rhinovirus-induced
asthma exacerbation and virus load in experimentally infected human volunteers. Induction by lipopolysaccharide in asthmatic macrophages was also deficient and correlated with exacerbation
severity. These results identify previously unknown mechanisms of susceptibility to infection in asthma and suggest new approaches to prevention and/or treatment of asthma exacerbations.
Access through your institution Buy or subscribe This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution ACCESS OPTIONS Access through your institution Subscribe to this
journal Receive 12 print issues and online access $209.00 per year only $17.42 per issue Learn more Buy this article * Purchase on SpringerLink * Instant access to full article PDF Buy now
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout ADDITIONAL ACCESS OPTIONS: * Log in * Learn about institutional subscriptions * Read our FAQs * Contact customer
support SIMILAR CONTENT BEING VIEWED BY OTHERS PROTECTIVE EFFECT OF INTERFERON TYPE I ON BARRIER FUNCTION OF HUMAN AIRWAY EPITHELIUM DURING RHINOVIRUS INFECTIONS IN VITRO Article Open access
16 December 2024 INTERFERON-DEPENDENT AND RESPIRATORY VIRUS-SPECIFIC INTERFERENCE IN DUAL INFECTIONS OF AIRWAY EPITHELIA Article Open access 24 June 2020 RHINOVIRUS-INDUCED EPITHELIAL RIG-I
INFLAMMASOME SUPPRESSES ANTIVIRAL IMMUNITY AND PROMOTES INFLAMMATION IN ASTHMA AND COVID-19 Article Open access 22 April 2023 REFERENCES * Corne, J.M. et al. _Lancet_ 359, 831–834 (2002).
Article Google Scholar * Talbot, T.R. et al. _N. Engl. J. Med._ 352, 2082–2090 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Wark, P. et al. _J. Exp. Med._ 201, 937–947 (2005). Article CAS
Google Scholar * Kotenko, S.V. et al. _Nat. Immunol._ 4, 69–77 (2003). Article CAS Google Scholar * Sheppard, P. et al. _Nat. Immunol._ 4, 63–68 (2003). Article CAS Google Scholar *
Spann, K.M., Tran, K.C., Chi, B., Rabin, R.L. & Collins, P.L. _J. Virol._ 78, 4363–4369 (2004). Article CAS Google Scholar * Johnston, S.L. et al. _Br. Med. J._ 310, 1225–1229 (1995).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Johnston, S.L. et al. _N. Engl. J. Med._ 354, 1589–1600 (2006). Article CAS Google Scholar * Yoneyama, M. et al. _Nat. Immunol._ 5, 730–737 (2004).
Article CAS Google Scholar * Carr, D.J., Tomanek, L., Silverman, R.H., Campbell, I.L. & Williams, B.R. _J. Virol._ 79, 9341–9345 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Yang, K. et
al. _Immunity_ 23, 465–478 (2005). Article CAS Google Scholar * Hewson, C.A., Jardine, A., Edwards, M.R., Laza-Stanca, V. & Johnston, S.L. _J. Virol._ 79, 12273–12279 (2005). Article
CAS Google Scholar * Fitzgerald, K.A. et al. _J. Exp. Med._ 198, 1043–1055 (2003). Article CAS Google Scholar * Illi, S. et al. _Br. Med. J._ 322, 390–395 (2001). Article CAS Google
Scholar Download references ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS M.C. was the recipient of a European Respiratory Society fellowship (LTRF2003-017). P.A.B.W. was supported by the National Health and Medical
Research Council Australia Neil Hamilton Fairley Fellowship. This work was supported by the Medical Research Council, UK: Clinical Research Professorship (to S.T.H.) & Clinical Research
Fellowship (to S.D.M. and S.L.J.), British Medical Association HC Roscoe Fellowships (to P.A.B.W. and S.D.M.), Asthma UK grant numbers 05/067 (to S.L.J.) and 03/031 (to P.A.B.W., D.E.D. and
S.T.H.), United States Public Health Services Grants AI051139 and AI057468 from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (to S.V.K.) and by British Lung Foundation/Severin
Wunderman Family Foundation Programme Grant 00/02 (to S.L.J.). AUTHOR INFORMATION Author notes * Marco Contoli and Simon D Message: These authors contributed equally to this work. AUTHORS
AND AFFILIATIONS * Department of Respiratory Medicine, National Heart and Lung Institute, Wright Fleming Institute of Infection and Immunity & MRC and Asthma UK Centre in Allergic
Mechanisms of Asthma, Imperial College London, Norfolk Place, W2 1PG, London, UK Marco Contoli, Simon D Message, Vasile Laza-Stanca, Michael R Edwards, Peter A B Wark, Nathan W Bartlett,
Tatiana Kebadze, Patrick Mallia, Luminita A Stanciu, Hayley L Parker, Louise Slater & Sebastian L Johnston * Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Research Centre on Asthma
and COPD, University of Ferrara, via Savonarola 9, Ferrara, 44100, Italy Marco Contoli & Alberto Papi * The Brooke Laboratories, Mailpoint 888, University of Southampton School of
Medicine, Southampton General Hospital, Southampton, SO16 6YD, UK Peter A B Wark, Stephen T Holgate & Donna E Davies * Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, Room E-641,
University of Medicine & Dentistry New Jersey - New Jersey Medical School, 185 South Orange Avenue, Newark, 07103, New Jersey, USA Anita Lewis-Antes * St Mary's NHS Trust, Praed
Street, London, W2 1NY, UK Onn M Kon & Sergei V Kotenko Authors * Marco Contoli View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Simon D Message
View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Vasile Laza-Stanca View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
* Michael R Edwards View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Peter A B Wark View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Nathan W Bartlett View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Tatiana Kebadze View author publications You can also
search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Patrick Mallia View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Luminita A Stanciu View author
publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Hayley L Parker View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Louise
Slater View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Anita Lewis-Antes View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google
Scholar * Onn M Kon View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Stephen T Holgate View author publications You can also search for this author
inPubMed Google Scholar * Donna E Davies View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Sergei V Kotenko View author publications You can also search
for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Alberto Papi View author publications You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar * Sebastian L Johnston View author publications
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar CONTRIBUTIONS M.C. performed all the laboratory work (except where stated performed by others) and statistical analyses and wrote
the first draft of the manuscript. S.D.M. performed all the patient recruitment for both the monocyte studies and the human experimental infection studies and performed the human infection
study. V.L.-S. performed the monocyte-derived macrophage experiments and assisted with the rest of the studies. M.R.E. designed the IFN-λ quantitative PCRs and assisted with the rest of the
studies. P.A.B.W. performed the patient recruitment and carried out the primary bronchial epithelial cell infection studies. N.W.B., T.K., P.M., L.A.S., H.L.P., L.S. and A.L.-A. assisted
with the studies. O.M.K. assisted in the patient recruitment and clinical conduct of the studies. S.T.H. and D.E.D. supervised and assisted in the conduct of the primary bronchial infection
study. S.V.K. advised on the scientific aspects of the IFN-λ studies and provided reagents. A.P. co-supervised the work of M.C. S.L.J. conceived, designed and supervised all the studies,
wrote the final draft of the manuscript and acts as guarantor for the studies. All authors contributed to the writing of the manuscript and have approved the final version for publication.
CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Correspondence to Sebastian L Johnston. ETHICS DECLARATIONS COMPETING INTERESTS Stephen T. Holgate and Donna E. Davies were cofounders of, hold shares in and are
consultants for, and Sebastian L. Johnston is a consultant for Synairgen PLC, which has an interest in developing interferons for treating respiratory diseases. Sebastian L. Johnston,
Stephen T. Holgate, Donna E. Davies, Peter A.B. Wark and Sergei V. Kotenko are inventors on patents relating to the use of interferons for treating respiratory diseases. SUPPLEMENTARY
INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. 1 IFN-λs are induced by rhinovirus infection of bronchial epithelial cells, monocytes and macrophages. (PDF 810 kb) SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. 2 IFN-λs induce
IFN-stimulated genes in and protect bronchial epithelial cells against rhinovirus infection _in vitro_. (PDF 636 kb) SUPPLEMENTARY TABLE 1 Demographic data for patients entering the clinical
studies. (PDF 45 kb) SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS (PDF 154 KB) SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE (PDF 158 KB) RIGHTS AND PERMISSIONS Reprints and permissions ABOUT THIS ARTICLE CITE THIS ARTICLE Contoli, M.,
Message, S., Laza-Stanca, V. _et al._ Role of deficient type III interferon-λ production in asthma exacerbations. _Nat Med_ 12, 1023–1026 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1462 Download
citation * Received: 18 January 2006 * Accepted: 11 July 2006 * Published: 13 August 2006 * Issue Date: 01 September 2006 * DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1462 SHARE THIS ARTICLE Anyone you
share the following link with will be able to read this content: Get shareable link Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Copy to clipboard Provided by the
Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative